Selection, proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow-derived liver stem cells with a culture system containing cholestatic serum in vitro
- PMID: 15484306
- PMCID: PMC4572301
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3308
Selection, proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow-derived liver stem cells with a culture system containing cholestatic serum in vitro
Abstract
Aim: To explore the feasibility of direct separation, selective proliferation and differentiation of the bone marrow-derived liver stem cells (BDLSC) from bone marrow cells with a culture system containing cholestatic serum in vitro.
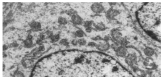
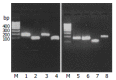
Methods: Whole bone marrow cells of rats cultured in routine medium were replaced with conditioning selection media containing 20 mL/L, 50 mL/L, 70 mL/L, and 100 mL/L cholestatic sera, respectively, after they attached to the plates. The optimal concentration of cholestatic serum was determined according to the outcome of the selected cultures. Then the selected BDLSC were induced to proliferate and differentiate with the addition of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). The morphology and phenotypic markers of BDLSC were characterized using immunohistochemistry, RT-PCR and electron microscopy. The metabolic functions of differentiated cells were also determined by glycogen staining and urea assay.
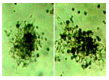
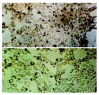
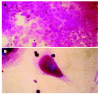
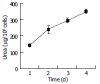
Results: Bone marrow cells formed fibroblast-like but not hepatocyte-like colonies in the presence of 20 mL/L cholestatic serum. In 70 mL/L cholestatic serum, BDLSC colonies could be selected but could not maintain good growth status. In 100 mL/L cholestatic serum, all of the bone marrow cells were unable to survive. A 50 mL/L cholestatic serum was the optimal concentration for the selection of BDLSC at which BDLSC could survive while the other populations of the bone marrow cells could not. The selected BDLSC proliferated and differentiated after HGF was added. Hepatocyte-like colony-forming units (H-CFU) then were formed. H-CFU expressed markers of embryonic hepatocytes (AFP, albumin and cytokeratin 8/18), biliary cells (cytokeratin 19), hepatocyte functional proteins (transthyretin and cytochrome P450-2b1), and hepatocyte nuclear factors (HNF-1alpha and HNF-3beta). They also had glycogen storage and urea synthesis functions, two of the critical features of hepatocytes.
Conclusion: The selected medium containing cholestatic serum can select BDLSC from whole bone marrow cells. It will be a new way to provide a readily available alternate source of cells for clinical hepatocyte therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Krause DS. Plasticity of marrow-derived stem cells. Gene Ther. 2002;9:754–758. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari G, Cusella-De Angelis G, Coletta M, Paolucci E, Stornaiuolo A, Cossu G, Mavilio F. Muscle regeneration by bone marrow-derived myogenic progenitors. Science. 1998;279:1528–1530. - PubMed
-
- Gussoni E, Soneoka Y, Strickland CD, Buzney EA, Khan MK, Flint AF, Kunkel LM, Mulligan RC. Dystrophin expression in the mdx mouse restored by stem cell transplantation. Nature. 1999;401:390–394. - PubMed
-
- Brazelton TR, Rossi FM, Keshet GI, Blau HM. From marrow to brain: expression of neuronal phenotypes in adult mice. Science. 2000;290:1775–1779. - PubMed
-
- Mezey E, Chandross KJ, Harta G, Maki RA, McKercher SR. Turning blood into brain: cells bearing neuronal antigens generated in vivo from bone marrow. Science. 2000;290:1779–1782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

