Relationship between serum trough infliximab levels, pretreatment C reactive protein levels, and clinical response to infliximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15485995
- PMCID: PMC1755482
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.030452
Relationship between serum trough infliximab levels, pretreatment C reactive protein levels, and clinical response to infliximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the relationship between serum trough infliximab levels and clinical response to infliximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
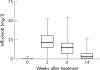
Methods: Disease activity and serum trough infliximab levels before and 2, 6, and 14 weeks after initiation of infliximab treatment at a dose of 3 mg/kg in a cohort of 105 patients with RA were assessed. Serum trough infliximab levels in responders and non-responders were compared. Additionally, the clinical responses of patients with high, intermediate, and low serum trough infliximab levels at 14 weeks were compared.
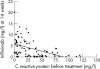
Results: After 14 weeks of treatment non-responders had lower serum trough levels of infliximab than responders (median (interquartile range) 0.5 (0.2-2.2) v 3.6 (1.4-8.2) mg/l; p<0.01)). Patients with low serum trough infliximab levels at 14 weeks had significantly less improvement in the 28 joint count Disease Activity Score (DAS28) score than patients with intermediate or high serum trough infliximab levels at 14 weeks. Pretreatment C reactive protein (CRP) levels correlated negatively with serum trough infliximab levels at 14 weeks after the start of treatment (Spearman rank correlation r(s) = -0.43, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Serum trough levels of infliximab correlate with the clinical response to treatment with infliximab and pretreatment CRP levels. This study indicates that patients with high pretreatment CRP levels might benefit from higher dosages of infliximab or shorter dosing intervals.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

