Acute type A aortic dissection in a cardiac allograft recipient: case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 15486115
- PMCID: PMC1768514
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2003.024307
Acute type A aortic dissection in a cardiac allograft recipient: case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Dissection of the ascending aorta is uncommon in cardiac allograft recipients and usually affects the native aorta. The diagnosis is often made at necropsy. The first case is reported of a Bentall procedure performed in a heart transplant recipient who presented with ascending aortic dissection of the donor aorta and concomitant aortic regurgitation seven years after orthotopic transplantation.
Figures
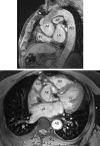
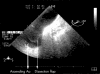

References
-
- Vigano’ M , Rinaldi M, D’Armini AM, et al. The spectrum of aortic complications after heart transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg 1999;68:105–8. - PubMed
-
- Derumeaux G , Habib G, Schleifer DM, et al. Standard orthotopic heart transplantation versus total orthotopic heart transplantation: a transesophageal echocardiography study of the incidence of left atrial thrombosis. Circulation 1995;92 (9 suppl) :H196–201. - PubMed
-
- Sahar G , Stamler A, Erez E, et al. Etiological factors influencing the development of atrioventricular valve incompetence after heart transplantation. Transplant Proc 1997;29:2675–6. - PubMed
-
- De Simone R , Lange R, Sack F-U, et al. Atrioventricular valve insufficiency and atrial geometry after orthotopic heart transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg 1995;60:1686–93. - PubMed
-
- Dreyfus G , Jebara VA, Couetil J, et al. Kinking of the pulmonary artery: a treatable cause of acute right ventricular failure after heart transplantation. J Heart Transplant 1990;9:575–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
