Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a target for small-molecule disease-modifying therapies in human neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 15486605
- PMCID: PMC518865
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a target for small-molecule disease-modifying therapies in human neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
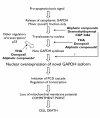
Recent articles have highlighted numerous additional functions of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) that are independent of its well-documented glycolytic function. One of the most intriguing of these functions is as an initiator of programmed cell death cascades. This activity involves a nuclear appearance of GAPDH, a considerable proportion of which requires synthesis of new GAPDH protein and has characteristics suggesting the involvement of a novel isozyme. The relevance of such findings to human neurodegenerative conditions is emphasized by the increased nuclear GAPDH observed in postmortem samples from patients with Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease and glaucoma, among others. A number of small-molecule compounds have now been identified that show anti-apoptotic activity because of their ability to interact with GAPDH and prevent its nuclear accumulation. These compounds, one of which is currently being tested in late-stage Phase II clinical trials as a disease-modifying therapy for Parkinson's disease, have potential utility in the treatment of human neurodegenerative conditions.
Des articles récents ont décrit de nombreuses fonctions supplémentaires de la glycéraldéhyde-3-phosphate déshydrogénase (GAPDH) indépendantes de sa fonction glycolytique bien documentée. Une des plus intrigantes de ces fonctions est celle de catalyseur de cascades d'apoptose. Cette activité met en cause une apparition dans le noyau de la GAPDH, dont une proportion importante nécessite la synthèse de nouvelle protéine de GAPDH et a des caractéristiques qui indiquent la présence d'un isozyme nouveau. L'élévation de la GAPDH nucléaire observée dans des échantillons postmortem prélevés chez des patients atteints de la maladie de Parkinson, la maladie d'Alzheimer, la chorée d'Huntington et le glaucome, notamment, met en évidence la pertinence de ces constatations dans le cas de problèmes neurodégénératifs humains. On a maintenant identifié un certain nombre de composés à petites molécules qui ont une activité anti-apoptotique parce qu'ils peuvent réagir avec la GAPDH et l'empêcher de s'accumuler dans le noyau. Ces composés, dont l'un fait actuellement l'objet d'essais cliniques de phase II, qui achèvent, comme traitement de fond contre la maladie de Parkinson, offrent des possibilités pour le traitement des maladies neurodégénératives humaines.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oxidatively modified glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in neurodegenerative processes and the role of low molecular weight compounds in counteracting its aggregation and nuclear translocation.Ageing Res Rev. 2018 Dec;48:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Ageing Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 30254002 Review.
-
Proapoptotic protein glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: a possible site of action of antiapoptotic drugs.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003 Apr;27(2):291-301. doi: 10.1016/S0278-5846(03)00024-1. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12657368 Review.
-
Alteration of intracellular structure and function of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: a common phenotype of neurodegenerative disorders?Neurotoxicology. 2002 Oct;23(4-5):603-9. doi: 10.1016/s0161-813x(02)00062-1. Neurotoxicology. 2002. PMID: 12428732 Review.
-
Role of the glycolytic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in normal cell function and in cell pathology.J Cell Biochem. 1997 Aug 1;66(2):133-40. J Cell Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9213215 Review.
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, apoptosis, and neurodegenerative diseases.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:269-90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.45.120403.095902. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15822178 Review.
Cited by
-
GAPDH is conformationally and functionally altered in association with oxidative stress in mouse models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.J Mol Biol. 2008 Oct 24;382(5):1195-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.07.088. Epub 2008 Aug 6. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18706911 Free PMC article.
-
Monoamine oxidase enzymes and oxidative stress in the rat optic nerve: age-related changes.Int J Exp Pathol. 2012 Dec;93(6):401-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2012.00832.x. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Int J Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23082958 Free PMC article.
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase versus toluidine blue as a marker for infarct volume estimation following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice.Exp Brain Res. 2006 Oct;175(1):60-7. doi: 10.1007/s00221-006-0526-3. Epub 2006 May 24. Exp Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16721606
-
Regulation of Autophagy by Nuclear GAPDH and Its Aggregates in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 26;20(9):2062. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092062. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31027346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Retinal Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15834. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115834. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sirover MA. Emerging new functions of the glycolytic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in mammalian cells. Life Sci 1996;58:2271-7. - PubMed
-
- Sirover MA. Role of the glycolytic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in normal cell function and in cell pathology. J Cell Biochem 1997;66:133-40. - PubMed
-
- Sirover MA. New insights into an old protein: the functional diversity of mammalian glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999;1432:159-84. - PubMed
-
- Berry MD, Boulton AA. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and apoptosis. J Neurosci Res 2000;60:150-4. - PubMed
-
- Lev N, Melamed E, Offen D. Apoptosis and Parkinson's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2003;27:245-50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
