Two Drosophila suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) differentially regulate JAK and EGFR pathway activities
- PMID: 15488148
- PMCID: PMC526380
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-5-38
Two Drosophila suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) differentially regulate JAK and EGFR pathway activities
Abstract
Background: The Janus kinase (JAK) cascade is an essential and well-conserved pathway required to transduce signals for a variety of ligands in both vertebrates and invertebrates. While activation of the pathway is essential to many processes, mutations from mammals and Drosophila demonstrate that regulation is also critical. The SOCS (Suppressor Of Cytokine Signaling) proteins in mammals are regulators of the JAK pathway that participate in a negative feedback loop, as they are transcriptionally activated by JAK signaling. Examination of one Drosophila SOCS homologue, Socs36E, demonstrated that its expression is responsive to JAK pathway activity and it is capable of downregulating JAK signaling, similar to the well characterized mammalian SOCS.
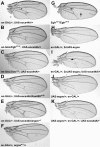
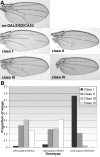
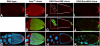
Results: Based on sequence analysis of the Drosophila genome, there are three identifiable SOCS homologues in flies. All three are most similar to mammalian SOCS that have not been extensively characterized: Socs36E is most similar to mammalian SOCS5, while Socs44A and Socs16D are most similar to mammalian SOCS6 and 7. Although Socs44A is capable of repressing JAK activity in some tissues, its expression is not regulated by the pathway. Furthermore, Socs44A can enhance the activity of the EGFR/MAPK signaling cascade, in contrast to Socs36E.
Conclusions: Two Drosophila SOCS proteins have some overlapping and some distinct capabilities. While Socs36E behaves similarly to the canonical vertebrate SOCS, Socs44A is not part of a JAK pathway negative feedback loop. Nonetheless, both SOCS regulate JAK and EGFR signaling pathways, albeit differently. The non-canonical properties of Socs44A may be representative of the class of less characterized vertebrate SOCS with which it shares greatest similarity.
Figures




References
-
- Peeters P, Raynaud SD, Cools J, Wlodarska I, Grosgeorge J, Philip P, Monpoux F, Van Rompaey L, Baens M, Van den Berghe H, Marynen P. Fusion of TEL, the ETS-variant gene 6 (ETV6), to the receptor- associated kinase JAK2 as a result of t(9;12) in a lymphoid and t(9;15;12) in a myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1997;90:2535–2540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

