Interhelical spacing in liquid crystalline spermine and spermidine-DNA precipitates
- PMID: 15489310
- PMCID: PMC1305016
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.040113
Interhelical spacing in liquid crystalline spermine and spermidine-DNA precipitates
Abstract
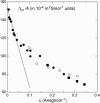
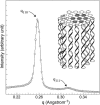
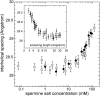
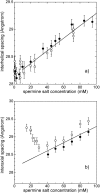
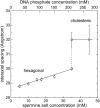
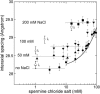
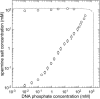
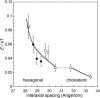
The structure of polyamines-DNA precipitates was studied by x-ray diffraction. Precise measurements of the interhelix distance a(H) were obtained at different NaCl, polyamine, and DNA concentrations. Most of the results were obtained using spermine and few others using spermidine. The precipitates are liquid crystalline, either hexagonal and/or cholesteric, with an interhelical spacing that depends on the ionic concentrations and on the polyamine type. In our experimental conditions, the spacing varies from 28.15 to 33.4 angstroms. This variation is interpreted in terms of different ionic components that are present inside the precipitates and that are thought to regulate the value of the cohesive energy of DNA. These results are discussed in relation to the biological processes requiring a closeness of double helices and to the role played by polyamine analogs in cancer therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyamine structural effects on the induction and stabilization of liquid crystalline DNA: potential applications to DNA packaging, gene therapy and polyamine therapeutics.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Sep 1;30(17):3722-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf503. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12202757 Free PMC article.
-
Selectivity of polyamines on the stability of RNA-DNA hybrids containing phosphodiester and phosphorothioate oligodeoxyribonucleotides.Biochemistry. 1999 Aug 17;38(33):10775-84. doi: 10.1021/bi990180t. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10451373
-
X-ray diffraction studies on cation-collapsed DNA.J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):313-29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90351-6. J Mol Biol. 1984. PMID: 6726812
-
Polyamines, chromatin structure and transcription.Bioessays. 1993 Aug;15(8):561-6. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150811. Bioessays. 1993. PMID: 8135771 Review.
-
[DNA liquid-crystalline dispersion particles as a basis for sensitive biosensor elements].Biofizika. 2004 May-Jun;49(3):468-85. Biofizika. 2004. PMID: 15327206 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Local structure of DNA toroids reveals curvature-dependent intermolecular forces.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Apr 19;49(7):3709-3718. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab197. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33784405 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-dependent DNA-DNA spacings in intact bacteriophage λ reflect relative importance of DNA self-repulsion and bending energies.Phys Rev Lett. 2011 Jan 14;106(2):028102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.028102. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Phys Rev Lett. 2011. PMID: 21405253 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-induced DNA condensation: choosing the model.Biophys J. 2005 Oct;89(4):2574-87. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.063909. Epub 2005 Aug 5. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 16085765 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and phase diagram of nucleosome core particles aggregated by multivalent cations.Biophys J. 2007 Nov 15;93(10):3652-63. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.108365. Epub 2007 Aug 10. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17693471 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and dynamic properties of linker histone H1 binding to DNA.Biomicrofluidics. 2011 Jun;5(2):24104. doi: 10.1063/1.3587096. Epub 2011 May 4. Biomicrofluidics. 2011. PMID: 21629560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeza, I., P. Gariglio, L. M. Rangel, P. Chavez, L. Cervantes, C. Arguello, C. Wong, and C. Montanez. 1987. Electron microscopy and biochemical properties of polyamine-compacted DNA. Biochemistry. 26:6387–6392. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield, V. A. 1996. DNA condensation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 6:334–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

