Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen
- PMID: 15489344
- PMCID: PMC523564
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.17.4.697-728.2004
Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen
Abstract
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a unique bacterium that does not always receive the attention it merits considering the number of illnesses it causes and the degree of morbidity associated with it in both children and adults. Serious infections requiring hospitalization, while rare, occur in both adults and children and may involve multiple organ systems. The severity of disease appears to be related to the degree to which the host immune response reacts to the infection. Extrapulmonary complications involving all of the major organ systems can occur in association with M. pneumoniae infection as a result of direct invasion and/or autoimmune response. The extrapulmonary manifestations are sometimes of greater severity and clinical importance than the primary respiratory infection. Evidence for this organism's contributory role in chronic lung conditions such as asthma is accumulating. Effective management of M. pneumoniae infections can usually be achieved with macrolides, tetracyclines, or fluoroquinolones. As more is learned about the pathogenesis and immune response elicited by M. pneumoniae, improvement in methods for diagnosis and prevention of disease due to this organism may occur.
Figures
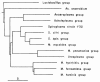

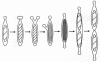

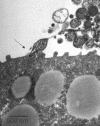

References
-
- Abele-Horn, M., W. Franck, U. Busch, H. Nitschko, R. Roos, and J. Heesemann. 1998. Transverse myelitis associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26:909-912. - PubMed
-
- Abramovitz, P., P. Schvartzman, D. Harel, I. Lis, and Y. Naot. 1987. Direct invasion of the central nervous system by Mycoplasma pneumoniae: a report of two cases. J. Infect. Dis. 155:482-487. - PubMed
-
- Agustin, E. T., V. Gill, and B. A. Cunha. 1994. Mycoplasma pneumoniae meningoencephalitis complicated by diplopia. Heart Lung 23:436-437. - PubMed
-
- Alexander, E. R., H. M. Foy, G. E. Kenny, R. A. Kronmal, R. McMahan, E. R. Clarke, W. A. MacColl, and J. T. Grayston. 1966. Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Its incidence in the membership of a co-operative medical group. N. Engl. J. Med. 275:131-136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

