Bacteriophage P1 in retrospect and in prospect
- PMID: 15489415
- PMCID: PMC523185
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7025-7028.2004
Bacteriophage P1 in retrospect and in prospect
Figures
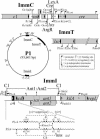
Comment on
-
Genome of bacteriophage P1.J Bacteriol. 2004 Nov;186(21):7032-68. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7032-7068.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15489417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arber, W., and D. Dussoix. 1962. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli. I. Host controlled modification of bacteriophage lambda. J. Mol. Biol. 5:18-36. - PubMed
-
- Bickle, T. A. 2004. Restricting restriction. Mol. Microbiol. 51:3-5. - PubMed
-
- Boyd, E. F., B. M. Davis, and B. Hochhut. 2001. Bacteriophage-bacteriophage interactions in the evolution of pathogenic bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 9:137-144. - PubMed
-
- Heinrich, J., M. Velleman, and H. Schuster. 1995. The tripartite immunity system of phages P1 and P7. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 17:121-126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

