Genome of bacteriophage P1
- PMID: 15489417
- PMCID: PMC523184
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7032-7068.2004
Genome of bacteriophage P1
Abstract
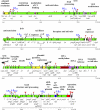
P1 is a bacteriophage of Escherichia coli and other enteric bacteria. It lysogenizes its hosts as a circular, low-copy-number plasmid. We have determined the complete nucleotide sequences of two strains of a P1 thermoinducible mutant, P1 c1-100. The P1 genome (93,601 bp) contains at least 117 genes, of which almost two-thirds had not been sequenced previously and 49 have no homologs in other organisms. Protein-coding genes occupy 92% of the genome and are organized in 45 operons, of which four are decisive for the choice between lysis and lysogeny. Four others ensure plasmid maintenance. The majority of the remaining 37 operons are involved in lytic development. Seventeen operons are transcribed from sigma(70) promoters directly controlled by the master phage repressor C1. Late operons are transcribed from promoters recognized by the E. coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme in the presence of the Lpa protein, the product of a C1-controlled P1 gene. Three species of P1-encoded tRNAs provide differential controls of translation, and a P1-encoded DNA methyltransferase with putative bifunctionality influences transcription, replication, and DNA packaging. The genome is particularly rich in Chi recombinogenic sites. The base content and distribution in P1 DNA indicate that replication of P1 from its plasmid origin had more impact on the base compositional asymmetries of the P1 genome than replication from the lytic origin of replication.
Figures





Comment in
-
Bacteriophage P1 in retrospect and in prospect.J Bacteriol. 2004 Nov;186(21):7025-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7025-7028.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15489415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abeles, A. L. 1986. P1 plasmid replication. Purification and DNA-binding activity of the replication protein RepA. J. Biol. Chem. 261:3548-3555. - PubMed
-
- Abeles, A. L., S. A. Friedman, and S. J. Austin. 1985. Partition of unit-copy miniplasmids to daughter cells. III. The DNA sequence and functional organization of the P1 partition region. J. Mol. Biol. 185:261-272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

