Alterations in gene expression associated with the overexpression of a splice variant of DNA methyltransferase 3b, DNMT3b4, during human hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 15490234
- PMCID: PMC12161791
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-004-0586-3
Alterations in gene expression associated with the overexpression of a splice variant of DNA methyltransferase 3b, DNMT3b4, during human hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
Purpose: Overexpression of a splice variant of DNA methyltransferase 3b, DNMT3b4, correlates significantly with DNA hypomethylation in pericentromeric satellite regions, which is known to result in centromeric decondensation and enhanced chromosomal recombination in precancerous conditions and hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs). We aimed to elucidate further the significance of DNMT3b4 during human hepatocarcinogenesis.
Methods: DNMT3b4-transfected human epithelial 293 cells were characterized using growth rate measurements, gene expression microarray, and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analyses. RT-PCR was also performed on eight normal liver specimens, 45 noncancerous liver specimens showing chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, which are considered to be precancerous conditions, and 56 HCCs.
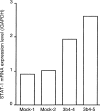
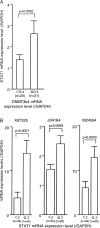
Results: The growth rate of the DNMT3b4 transfectants was about double that of mock-transfectants. Induction of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), an effector of interferon signaling, and of a set of downstream genes implicated in such signaling, was observed in the DNMT3b4 transfectants. There was significant correlation between the mRNA expression levels of DNMT3b4 and STAT1 in HCCs. mRNA expression levels of STAT1 and the three downstream genes examined were all significantly elevated in the chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis specimens compared with the normal liver specimens. Among the HCCs, the mRNA expression levels of STAT1 and the downstream genes were higher in tumors without portal vein involvement than in more malignant HCCs with portal vein involvement. Significant correlations between the mRNA expression levels of STAT1 and each of the downstream genes were observed in the tissue samples.
Conclusions: Overexpression of DNMT3b4 is involved in human hepatocarcinogenesis, even at the precancerous stages, not only by inducing chromosomal instability but also by affecting the expression of specific genes.
Figures


References
-
- Aizawa K, Motoyama T, Watanabe H (1989) Placental alkaline phosphatase-like isoenzymes produced by human gastric cancer cells. Acta Pathol Jpn 39:630–637 - PubMed
-
- Alexander JJ, Bey EM, Geddes EW, Lecatsas G (1976) Establishment of a continuously growing cell line from primary carcinoma of the liver. S Afr Med J 50:2124–2128 - PubMed
-
- Calo V, Migliavacca M, Bazan V, Macaluso M, Buscemi M, Gebbia N, Russo A (2003) STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol 197:157–168 - PubMed
-
- Chuang LS, Ian HI, Koh TW, Ng HH, Xu G, Li BF (1997) Human DNA-(cytosine-5) methyltransferase-PCNA complex as a target for p21WAF1. Science 277:1996–2000 - PubMed
-
- Eguchi K, Kanai Y, Kobayashi K, Hirohashi S (1997) DNA hypermethylation at the D17S5 locus in non-small cell lung cancers: its association with smoking history. Cancer Res 57:4913–4915 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

