Central tolerance to tissue-specific antigens mediated by direct and indirect antigen presentation
- PMID: 15492126
- PMCID: PMC2211843
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041457
Central tolerance to tissue-specific antigens mediated by direct and indirect antigen presentation
Abstract
Intrathymic expression of tissue-specific antigens (TSAs) by medullary thymic epithelial cells (Mtecs) leads to deletion of autoreactive T cells. However, because Mtecs are known to be poor antigen-presenting cells (APCs) for tolerance to ubiquitous antigens, and very few Mtecs express a given TSA, it was unclear if central tolerance to TSA was induced directly by Mtec antigen presentation or indirectly by thymic bone marrow (BM)-derived cells via cross-presentation. We show that professional BM-derived APCs acquire TSAs from Mtecs and delete autoreactive CD8 and CD4 T cells. Although direct antigen presentation by Mtecs did not delete the CD4 T cell population tested in this study, Mtec presentation efficiently deleted both monoclonal and polyclonal populations of CD8 T cells. For developing CD8 T cells, deletion by BM-derived APC and by Mtec presentation occurred abruptly at the transitional, CD4high CD8low TCRintermediate stage, presumably as the cells transit from the cortex to the medulla. These studies reveal a cooperative relationship between Mtecs and BM-derived cells in thymic elimination of autoreactive T cells. Although Mtecs synthesize TSAs and delete a subset of autoreactive T cells, BM-derived cells extend the range of clonal deletion by cross-presenting antigen captured from Mtecs.
Figures


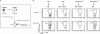

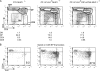
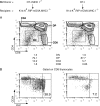
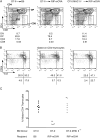
References
-
- Webb, S.R., and J. Sprent. 1990. Tolerogenicity of thymic epithelium. Eur. J. Immunol. 20:2525–2528. - PubMed
-
- Derbinski, J., A. Schulte, B. Kyewski, and L. Klein. 2001. Promiscuous gene expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells mirrors the peripheral self. Nat. Immunol. 2:1032–1039. - PubMed
-
- Smith, K.M., D.C. Olson, R. Hirose, and D. Hanahan. 1997. Pancreatic gene expression in rare cells of thymic medulla: evidence for functional contribution to T cell tolerance. Int. Immunol. 9:1355–1365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

