Modeling of cell signaling pathways in macrophages by semantic networks
- PMID: 15494071
- PMCID: PMC528732
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-156
Modeling of cell signaling pathways in macrophages by semantic networks
Abstract
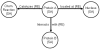
Background: Substantial amounts of data on cell signaling, metabolic, gene regulatory and other biological pathways have been accumulated in literature and electronic databases. Conventionally, this information is stored in the form of pathway diagrams and can be characterized as highly "compartmental" (i.e. individual pathways are not connected into more general networks). Current approaches for representing pathways are limited in their capacity to model molecular interactions in their spatial and temporal context. Moreover, the critical knowledge of cause-effect relationships among signaling events is not reflected by most conventional approaches for manipulating pathways.
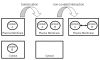
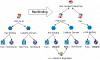
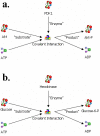
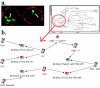
Results: We have applied a semantic network (SN) approach to develop and implement a model for cell signaling pathways. The semantic model has mapped biological concepts to a set of semantic agents and relationships, and characterized cell signaling events and their participants in the hierarchical and spatial context. In particular, the available information on the behaviors and interactions of the PI3K enzyme family has been integrated into the SN environment and a cell signaling network in human macrophages has been constructed. A SN-application has been developed to manipulate the locations and the states of molecules and to observe their actions under different biological scenarios. The approach allowed qualitative simulation of cell signaling events involving PI3Ks and identified pathways of molecular interactions that led to known cellular responses as well as other potential responses during bacterial invasions in macrophages.
Conclusions: We concluded from our results that the semantic network is an effective method to model cell signaling pathways. The semantic model allows proper representation and integration of information on biological structures and their interactions at different levels. The reconstruction of the cell signaling network in the macrophage allowed detailed investigation of connections among various essential molecules and reflected the cause-effect relationships among signaling events. The simulation demonstrated the dynamics of the semantic network, where a change of states on a molecule can alter its function and potentially cause a chain-reaction effect in the system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis modulators of the macrophage's cellular events.Microbes Infect. 2012 Nov;14(13):1211-9. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22841679 Review.
-
IRAK-M alters the polarity of macrophages to facilitate the survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Aug 23;17(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-1095-2. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28835201 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3463 induces mycobactericidal activity in macrophages by enhancing phagolysosomal fusion and exhibits therapeutic potential.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 12;9(1):4246. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38982-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30862819 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-exposure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages to crystalline silica impairs control of bacterial growth by deregulating the balance between apoptosis and necrosis.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 22;8(11):e80971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080971. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278357 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the macrophage: maintaining a balance.Cell Host Microbe. 2008 Jun 12;3(6):399-407. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.05.006. Cell Host Microbe. 2008. PMID: 18541216 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying a biomarker network for corticosteroid resistance in asthma from bronchoalveolar lavage samples.Mol Biol Rep. 2016 Jul;43(7):697-710. doi: 10.1007/s11033-016-4007-x. Epub 2016 May 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27188427
References
-
- BioCarta http://www.biocarta.com
-
- Signal Transduction Knowledge Environment (STKE) http://stke.sciencemag.org/ - PubMed
-
- Kitano H. The standard graphical notation for biochemical networks. ICSB-2002 workshop on SBML/SBW (Stockholm) 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

