Clotiapine for acute psychotic illnesses
- PMID: 15495032
- PMCID: PMC8985500
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002304.pub2
Clotiapine for acute psychotic illnesses
Abstract
Background: Acute psychotic illnesses, especially when associated with agitated or violent behaviour, require urgent pharmacological tranquillisation or sedation. Clotiapine, a dibenzothiazepine neuroleptic, is being used for this purpose in several countries.
Objectives: To estimate the effects of clotiapine when compared to other 'standard' or 'non-standard' treatments for acute psychotic illnesses in controlling disturbed behaviour and reducing psychotic symptoms.
Search strategy: We updated previous searches by searching the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group Register (April 2004)
Selection criteria: The review included randomised clinical trials comparing clotiapine with any other treatment for people with acute psychotic illnesses.
Data collection and analysis: Relevant studies were selected for inclusion, their quality was assessed and data extracted. Data were excluded where more than 50% of participants in any group were lost to follow up. For binary outcomes we calculated a standard estimation of the risk ratio (RR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI). For continuous outcomes, endpoint data were preferred to change data. Non-skewed data from valid scales were summated using a weighted mean difference (WMD).
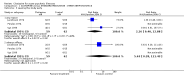
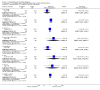
Main results: We identified five relevant trials. None compared clotiapine with placebo, but control drugs were either antipsychotics (chlorpromazine, perphenazine, trifluoperazine and zuclopenthixol acetate) or benzodiazepines (lorazepam). Versus the antipsychotics, the results for 'no important global improvement' did not suggest clotiapine to be superior, or inferior, to chlorpromazine, perphenazine, or trifluoperazine (n = 83, 3 RCTs, RR 0.82 CI 0.22 to 3.05, I-squared 58%). Use of clotiapine when compared with chlorpromazine did change the proportion of people ready for hospital discharge by the end of the study (n = 49, 1 RCT, RR 1.04 95%CI 0.96 to 2.12). Overall, attrition rates were low. No significant difference was found for those allocated to clotiapine compared with people randomised to other antipsychotics (n = 121, RR 2.26 95%CI 0.40 to 13). Weak data suggests that clotiapine may result in less need for antiparkinsonian treatment compared with zuclopenthixol acetate (n = 38, RR 0.43 95%CI 0.02 to 0.98). Compared with lorazepam, clotiapine, when used to control aggressive/violent outbursts for people already treated with haloperidol, did not significantly improve mental state (WMD -3.36 95%CI -8.09 to 1.37). We could not pool much data due to skew or inadequate presentation of results. Economic outcomes and satisfaction with care were not addressed.
Reviewers' conclusions: We found no evidence to support the use of clotiapine in preference to other 'standard' or 'non-standard' treatments for management of people with acute psychotic illness. All trials in this review have important methodological problems. We do not wish to discourage clinicians from using clotiapine in the psychiatric emergency, but well-designed, conducted and reported trials are needed to properly determine the efficacy of this drug.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures





Update of
-
Clotiapine for acute psychotic illnesses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD002304. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002304. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD002304. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002304.pub2. PMID: 11279762 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Itoh 1969 {published data only}
-
- Itoh H, Okamoto M, Miura S, Suzuki Y, Takemasa K, Shigeta M, Mochizuki N, Yagi G, Asaka H. A comparison between the clinical effectiveness of a dibenzothiazepine derivative and a phenothiazine derivative in schizophrenia. A controlled double‐blind study using clothiapine (W‐130) and perphenazine. Seishin Igaku 1969;11:465‐75.
-
- Itoh H, Okamoto T, Miura S, Suzuki Y, Takemasa K, Shigeta M, Mochizuki M, Yagi G, Asaka H. Comparison of a dibenzothiazepine derivative (clothiapine = w‐130) and a phenothiazine derivative (perphenazine) in schizophrenic patients using double‐blind technique [[data not available]]. Seishin Igaku 1969;11(6):465‐75. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 4939829]
Jacobsson 1974 {published data only}
-
- Jacobsson L, Noren MB, Perris C, Rapp W. A controlled trial of clothiapine and chlorpromazine in acute schizophrenic syndromes. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1974;255:55‐70. - PubMed
Perales 1974 {published data only}
-
- Perales CJA, Garcia MA, Infantes PV, Valle EDG. Comparative study between clothiapine and trifluoperazine in acute episodes of paranoid schizophrenia [Estudio comparativo de la clotiapina y de la trifluoperazina en episodios agudos de esquizofrenia paranoide]. Acta Psiquiatrica y Psicologica de America Latina 1974;20(3):207‐13. - PubMed
Subramaney 1998 {published data only}
-
- Subramaney U, Brook S, Berk M. A prospective randomised double blind controlled study of the efficacy of lorazepam versus Clothiapine in the control of acutely behaviourally disturbed patients. 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1997 Sep 13‐17; Vienna, Austria. 1997. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 4939829]
-
- Subramaney U, Brook S, Berk M. A prospective randomised double‐blind controlled study of the efficacy of lorazepam versus clothiapine in the control of acutely behaviourally disturbed patients. South African Medical Journal 1998;88(3):307‐10.
Uys 1996 {unpublished data only}
-
- Uys H, Berk M. A controlled double blind study of zuclopenthixol acetate compared to clothiapine in acute psychosis including mania and exacerbation of chronic psychosis. Proceedings of XXth Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum, Melbourne, Australia. June 1996.
-
- Uys H, Berk M. A controlled double blind study of zuclopenthixol acetate compared to clothiapine in acute psychosis including mania and exacerbation of chronic psychosis. Unpublished Report 1996. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 4939829]
References to studies excluded from this review
Bellomo 1973 {published data only}
-
- Bellomo LE. Clinical study with clothiapine in psychotic patients [Experiencia clínica con clotiapina en enfermos psicoticos]. La Semana Medica 1973;143:887‐90.
Bellomo 1975 {published data only}
-
- Bellomo L, Faleni R, Merzbacher B. Clinical study of a new dibenzothiazepine derivative in patients with acute psychoses [Investigacion clínica con un nuevo derivado dibenzotiacepínico en pacientes psicoticos agudos]. La Semana Medica 1975;146:202‐6.
Bente 1966 {published data only}
-
- Bente D, Engelmeier MP, Heinrich K, Hippius H, Schmitt W. Clinical studies with a neuroleptic dibenzothiazepine derivative [Klinische Untersuchungen mit einem neuroleptisch wirksamen Dibenzothiazepin‐Derivat]. Arzneimittel‐Forschung/Drug Research 1966;16:314‐6. - PubMed
Block 1974 {published data only}
-
- Block C, Borendal‐Jansson B, Carlsson C. A double‐blind crossover comparison between clothiapine and diazepam in the treatment of mental symptoms in chronic alcoholics. International journal of clinical pharmacology, therapy and toxicology 1974;9:321‐5. - PubMed
Caldas 1971 {published data only}
-
- Caldas U, Naitzke JC, Zucchi J. Clinical study with a dibenzothiazepine derivative, HF 2159 (Entumine) [Ensaio clínico com um derivado das dibenzotiazepinas‐HF 2159 (Entumina)]. Folha Medica 1971;62(3):385‐92.
Cante 1971 {published data only}
-
- Cante C, Marocchino R. Clinical evaluation of HF 2159 in psychiatric therapy [Valutazione clinica dell'HF 2159 in terapia psichiatrica]. Ospedale Psichiatrica 1971;39(2):347‐77. - PubMed
Carra 1974 {published data only}
-
- Carra G, Pereyra S, Pangas JC. Clinical experiences with clothiapine [Experiencia clínica con la clotiapina]. La Semana Medica 1974;144:169‐79.
Delay 1965 {published data only}
-
- Delay J, Deniker P, Ginestet D, Peron P, Verdeaux J. Investigations into new neuroleptics: efficacy of a dibenzothiazepine (H.F. 21.59) [Recherches concernant de nouveaux composes neuroleptiques: efficacite d'une dibenzothiazepine (H.F. 21.59)]. Encephale 1965;54:525‐31. - PubMed
Etienne 1976 {published data only}
-
- Etienne T, Guittet JP, Veyssiere M, Vultaggio R. Clothiapine in states of agitation [La clotiapine dans les etats d'agitation]. Actualites Psychiatriques 1976;6(3):81‐5.
Gazzaniga 1972 {published data only}
-
- Gazzaniga G, Galavotti B. Clinical study of the anxiolytic effect of Entumin [Sperimentazione clinica della proprieta ansiolitiche dell' Entumin]. Rassegna di Studi Psichiatrici 1972;61:601‐8.
Gehring 1972 {published data only}
-
- Gehring HR. Emergency treatment in juvenile drug consumers [Notfalltherapie bei jugendlichen Drogenkonsumenten]. Schweizerische Arztezeitung 1972;53:1729‐32.
Giordano 1973 {published data only}
-
- Giordano G. Clinical study of the therapeutic efficacy of Entumin [Saggio clinico sull'attivita terapeutica dell'Entumin]. Rivista di Neuropsichiatria e Scienze Affini 1973;19:143‐9.
Kammerer 1967 {published data only}
-
- Kammerer T, Singer L, Sichel JP, Gurfein L, Wysoki V. LW. 2159 (Etumine) Experimentation and clinical control by a new method of statistical analysis using computers electroniques [L.W. 2159 (Etumine): experimentation clinique et controle par une nouvelle methode d'exploitation statistique utilisant les ordinateurs electroniques]. Annales medico psychologiques 1967;125:290‐6. - PubMed
Kaneko 1969 {published data only}
-
- Kaneko J, Tanimukai H, Kudo Y. A double‐blind, controlled study of the effects of clothiapine and chlorpromazine on schizophrenia [(Original Japanese)]. Clinical Psychiatry 1969;11:721‐8.
Martin 1968 {published data only}
-
- Martin A, Houdret JC, Touron P, Masson JM. Clinical study of a new neuroleptic, a dibenzothiazepine derivative [Etude clinique d'un nouveau neuroleptique derive de la dibenzothiazepine]. Annales medico‐psychologiques 1968;126(2):381‐8. - PubMed
Martins 1969 {published data only}
-
- Martins C, Modesto Gil A, Signorini J, Cortez Vieira N. Clinical study with Entumine in hospitalized patients [Ensaio clínico com a Etumina em pacientes hospitalizados]. Revista brasileira de Psiquiatria 1969;3(4):221‐5.
Matsushita 1968 {published data only}
-
- Matsushita T, Ohgishi TA. Clinical experience of clothiapine in schizophrenia [(Original Japanese)]. Medical Consultation and New Remedies 1968;5:1947‐54.
Ohkuma 1970 {published data only}
-
- Ohkuma F, Takamuro S, Takahashi T, Fukui S. Clinical trials of clothiapine by parenteral route of administration (intramuscular injection) [(Original Japanese)]. Journal of Remedies and Clinics 1970;19:55‐9.
Oules 1973 {published data only}
-
- Oules J, Bataille J. Contribution to the study of clothiapine in psychiatry [Contribution a l'etude de la clotiapine en psychiatrie]. Actualites psychiatriques. Supplement therapeutique 1973;3(4):12‐4.
Rapidis 1975 {published data only}
-
- Rapidis P, Krystallis A. Clinical assessment of the sedative and antipsychotic activity of Entumine [Evaluation clinique de l'action sedative et antipsychotique de l'Entumine (Orig. en langue grecque)]. Galenos 1975;17:488‐94.
Rodova 1971 {published data only}
-
- Rodova A, Nahunek K, Svestka J. Comparison of the therapeutic efficiency of clothiapin and perphenazine in schizophrenic patients. Scripta Medica 1971;44:241‐8.
Rosier 1974 {published data only}
-
- Rosier YA. Clinical study of injectable clothiapine [Etude clinique de la clotiapine injectable]. Lyon Medical 1974;231:271‐3.
Savoldi 1967 {published data only}
-
- Savoldi F, Arrigo A, Mille T, Tartara A. Clinical study of a new neuroleptic (Wander HF 2159) [Studio clinico di una nuova sostanza neurolettica (Wander HF 2159)]. La Riunione Nazionale della Societa Italiana di Neuropsicofarmacologia. 1967:7‐12.
Toerien 1973 {published data only}
-
- Toerien I. Clotiapine in the management of alcoholism and drug addiction: report on a clinical trial. Med. Proc. 1973;19(1):4‐8.
Traldi 1969 {published data only}
-
- Traldi S. Clinical study on a dibenzothiazepine derivative with neuroleptic activity: clothiapine [Ensaio clínico com um derivado dibenzotiazepínico de acão neuroleptica: a clotiapina]. Folha Medica 1969;59:407‐15.
Van Wyk 1971 {published data only}
-
- Wyk AJ, Marais GF. Chlorpromazine, clotiapine and thioridazine‐a comparative clinical trial on Bantu psychotic patients. South African Medical Journal 1971;45(34):945‐7. - PubMed
Watanabe 1969 {published data only}
-
- Watanabe M, Nimiya A, Edamatsu K, Johma S, Kohno T, Ehara T, Ohara Y. Clinical experiences of W‐130 (clothiapine) in various psychotic patients [(Original Japanese)]. Shinryo (Medical Consultation) 1969;22:1455‐60.
Zapletalek 1971 {published data only}
-
- Zapletalek M, Rikovsky S, Mrna B. Clinical experience with clothiapin (Entumin) in schizophrenic psychoses. Activitas Nervosa Superior (Praha) 1971;13:181‐2. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ayuso‐Gutierrez 1973 {published data only}
-
- Ayuso‐Gutierrez JL, Alvarez‐Egocheaga L. Therapeutic evaluation of Clothiapine in various psychopathological patterns [Valoracion terapeutica de la Clotiapina en diversos cuadros psicopatologicos]. Actas Luso Esp. Neurol. Psiquiatr. Cienc. Afines 1973;1(4):565‐70. - PubMed
Belmaker 2009 {published data only}
-
- Belmaker R. Clotiapine for schizophrenia. Stanley Foundation Research Programs 2009.
Geller 2005 {published data only}
-
- Geller V, Gorzaltsan I, Shleifer T, Belmaker RH, Bersudsky Y. Clotiapine compared with chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2005;80(2‐3):343‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nahunek 1981 {published data only}
-
- Nahunek K, Svestka J, Ceskova E. On the question of differences between therapeutic responses after particular neuroleptics in comparison to perphenazine in schizophrenics [Kotazce rozdilnosti terapeutickych odpovedi po jednotlivych neurolepticich ve srovnani s perphenazinem u schizofrennich nemocnych]. Ceskoslovenska Psychiatrie 1981;77(1):25‐30. [MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO 68‐01789; PMID 6113897] - PubMed
Schliefer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Schliefer T, Bersudsky Y, Geller V, Belmaker RH. Clotiapine in schizophrenia: a controlled study. Proceedings of the 16th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 2003 Sep 20‐24; Prague, Czech Republic. 2003.
Additional references
Altman 1996
Axelsson 1992
-
- Axelsson R, Lagerkvist‐Briggs M. Factors predicting suicide in psychotic patients. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 1992;241(5):259‐66. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Binder 1999
-
- Binder RL, McNiel DE. Contemporary practices in managing acute violent patients in 20 psychiatric emergency rooms. Psychiatric Services 1999;50(12):1553‐4. - PubMed
Bland 1997
Chalmers 1983
-
- Chalmers TC, Celano P, Sacks HS, Smith H. Bias in treatment assignment in controlled clinical trials. New England Journal of Medicine 1983;309(22):1358‐61. - PubMed
Chouinard 1993
-
- Chouinard G, Annable L, Turnier L, Holobow N, Szkrumelak N. A double‐blind randomized clinical trial of rapid tranquilisation with I.M. Clonazepam and I.M. haloperidol in agitated psychotic patients with manic symptoms. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1993;38(Supplement 4):S114‐S121. - PubMed
Clarke 2003
-
- Clarke M, Oxman AD. Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook 4.2.0 [updated March 2003]. The Cochrane Library 2003, Issue Issue 2.
Cunnane 1994
-
- Cunnane JG. Drug management of disturbed behaviour by psychiatrists. Psychiatric Bulletin 1994;18:138‐9.
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Dorevitch 1999
-
- Dorevitch A, Katz N, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Weizman A. Intramuscular flunitrazepam versus intramuscular haloperidol in the emergency treatment of aggressive psychotic behavior. American Journal of Psychiatry 1999;156(1):142‐4. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Fisher 1993
-
- Fisher S, Greenberg RP. How sound is the double‐blind design for evaluating psychotropic drugs?. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1993;181(6):345‐50. - PubMed
Greenberg 1992
-
- Greenberg RP, Bornstein RF, Greenberg MD, Fisher S Greenberg RP, Bornstein RF, Greenberg MD, Fisher S Greenberg RP, Bornstein RF, Greenberg MD, Fisher S Greenberg RP, Bornstein RF, Greenberg MD, Fisher S. A meta‐analysis of antidepressant outcome under "blinder" conditions. Journal of Consultation and Clinical Psychology 1992;60(5):664‐9. - PubMed
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83 876‐83. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Hu 1991
-
- Hu WH, Sun CM, Lee CT, Peng SL, Lin SK, Shen WW. A clinical study of schizophrenic suicides. Forty‐two cases in Taiwan. Schizophrenia Research 1991;5(1):43‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Huf 2002a
Huf 2002b
Hughes 1999
-
- Hughes DH. Acute psychopharmacological management of the aggressive psychotic patient. Psychiatric Services 1999;50(9):1135‐7. - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled clinical trials. Vol. 17, New York: Elsevier, 1996:1‐12. - PubMed
Krakowski 1999
-
- Krakowski M, Czobor P, Chou JC. Course of violence in patients with schizophrenia: relationship to clinical symptoms. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1999;25(3):505‐17. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lokshin 1998
-
- Lokshin P, Kotler M, Kutzuk D, Belmaker RH. Clotiapine: an old neuroleptic with possible clozapine‐like properties. Progress in Neuro‐Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 1998;22:1293‐8.
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987‐91. - PubMed
Moritz 1999
-
- Moritz F, Bauer F, Boyer P, Lemarchand P, Kerleau JM, Moirot E, Navarre C, Muller JM. No English title available [Les patients agites au service d'accueil et d'urgence du CHU de Rouen]. La Presse Medicale 1999;28(30):1630‐4. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Pilowsky 1992
-
- Pilowsky LS, Ring H, Shine PJ, Battersby M, Lader M. Rapid tranquillisation. A survey of emergency prescribing in a general psychiatric hospital. British Journal of Psychiatry 1992;160:831‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson GM, Angus JWS. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica ‐ Supplementum 1970;45:11‐9. - PubMed
Taylor 1985
-
- Taylor PJ. Motives for offending among violent and psychotic men. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;147:491‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Taylor 1998
-
- Taylor PJ, Leese M, Williams D, Butwell M, Daly R, Larkin E. Mental disorder and violence. A special (high security) hospital study. British Journal of Psychiatry 1998;172:218‐26. - PubMed
Tiihonen 1997
-
- Tiihonen J, Isohanni M, Rasanen P, Koiranen M, Moring J. Specfic major mental disorders and criminality: a 26‐year prospective study of the 1966 northern Finland birth cohort. American Journal of Psychiatry 1997;154(6):840‐5. - PubMed
TREC 2003
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organistation‐based intervention in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐75. - PubMed
Yudofsky 1986
-
- Yudofsky SC, Silver JM, Jackson W, Endicott J, Williams D. The Overt Aggression Scale for the objective rating of verbal and physical aggression. American Journal of Psychiatry 1986;143:35‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

