Each sensory nerve arising from the geniculate ganglion expresses a unique fingerprint of neurotrophin and neurotrophin receptor genes
- PMID: 15495212
- PMCID: PMC2804271
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.20297
Each sensory nerve arising from the geniculate ganglion expresses a unique fingerprint of neurotrophin and neurotrophin receptor genes
Abstract
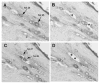
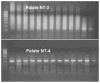
Neurons in the geniculate ganglion, like those in other sensory ganglia, are dependent on neurotrophins for survival. Most geniculate ganglion neurons innervate taste buds in two regions of the tongue and two regions of the palate; the rest are cutaneous nerves to the skin of the ear. We investigated the expression of four neurotrophins, nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin 3 (NT-3), and NT-4, and five neurotrophin receptors, trkA, trkB, trkC, p75, and truncated trkB (Trn-B) in single sensory neurons of the adult rat geniculate ganglion associated with the five innervation fields. For fungiform papillae, a glass pipette containing biotinylated dextran was placed over the target papilla and the tracer was iontophoresed into the target papilla. For the other target fields, Fluoro-Gold was microinjected. After 3 days, geniculate ganglia were harvested, sectioned, and treated histochemically (for biotinylated dextran) or immunohistochemically (for Fluoro-Gold) to reveal the neurons containing the tracer. Single labeled neurons were harvested from the slides and subjected to RNA amplification and RT-PCR to reveal the neurotrophin or neurotrophin receptor genes that were expressed. Neurons projecting from the geniculate ganglion to each of the five target fields had a unique expression profile of neurotrophin and neurotrophic receptor genes. Several individual neurons expressed more than one neurotrophin receptor or more than one neurotrophin gene. Although BDNF is significantly expressed in taste buds, its primary high affinity receptor, trkB, was not prominently expressed in the neurons. The results are consistent with the interpretation that at least some, perhaps most, of the trophic influence on the sensory neurons is derived from the neuronal somata, and the trophic effect is paracrine or autocrine, rather than target derived. The BDNF in the taste bud may also act in a paracrine or autocrine manner on the trkB expressed in taste buds, as shown by others.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Embryonic geniculate ganglion neurons in culture have neurotrophin-specific electrophysiological properties.Neuroscience. 2003;118(1):145-59. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00814-x. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12676146
-
Mice with a targeted disruption of the neurotrophin receptor trkB lose their gustatory ganglion cells early but do develop taste buds.Int J Dev Neurosci. 1997 Jul;15(4-5):563-76. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(96)00111-6. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9263033
-
The transcription factor Phox2b distinguishes between oral and non-oral sensory neurons in the geniculate ganglion.J Comp Neurol. 2017 Dec 15;525(18):3935-3950. doi: 10.1002/cne.24312. Epub 2017 Sep 15. J Comp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28856690 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of neurotrophin receptors and ligands in vertebrate neurons: tools for evolutionary stability or changes in neural circuits?Brain Behav Evol. 2006;68(3):157-72. doi: 10.1159/000094085. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Brain Behav Evol. 2006. PMID: 16912469 Review.
-
Building sensory receptors on the tongue.J Neurocytol. 2004 Dec;33(6):631-46. doi: 10.1007/s11068-005-3332-0. Epub 2005 Oct 11. J Neurocytol. 2004. PMID: 16217619 Review.
Cited by
-
Taste bud-derived BDNF maintains innervation of a subset of TrkB-expressing gustatory nerve fibers.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jul;82:195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28600222 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that regulate embryonic gustatory development.BMC Neurosci. 2007 Sep 18;8 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-S3-S4. BMC Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17903280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taste Bud-Derived BDNF Is Required to Maintain Normal Amounts of Innervation to Adult Taste Buds.eNeuro. 2015 Dec 31;2(6):ENEURO.0097-15.2015. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0097-15.2015. eCollection 2015 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2015. PMID: 26730405 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial overexpression of BDNF and NT4 produces distinct gustatory axon morphologies that disrupt initial targeting.Dev Biol. 2006 Apr 15;292(2):457-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.01.021. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16500639 Free PMC article.
-
Taste neurons consist of both a large TrkB-receptor-dependent and a small TrkB-receptor-independent subpopulation.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 27;8(12):e83460. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083460. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alderson RF, Curtis R, Alterman AL, Lindsay RM, DiStefano PS. Truncated TrkB mediates the endocytosis and release of BDNF and neurotrophin-4/5 by rat astrocytes and Schwann cells in vitro. Brain Res. 2000;871:210–222. - PubMed
-
- Armanini MP, McMahon SB, Sutherland J, Shelton DL, Philips HS. Truncated and catalytic isoforms of trkB are co-expressed in neurons of rat and mouse CNS. Eur J Neurosci. 1995;7:1403–1409. - PubMed
-
- Barbacid M. The trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J Neurobiol. 1994;25:1386–1403. - PubMed
-
- Bibel M, Barde YA. Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2929–2937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

