NEDD4-2 (neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4-2) negatively regulates TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) signalling by inducing ubiquitin-mediated degradation of Smad2 and TGF-beta type I receptor
- PMID: 15496141
- PMCID: PMC1134864
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040738
NEDD4-2 (neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4-2) negatively regulates TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) signalling by inducing ubiquitin-mediated degradation of Smad2 and TGF-beta type I receptor
Abstract
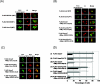
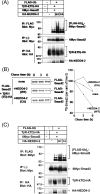
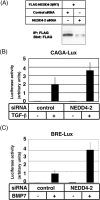
Inhibitory Smad, Smad7, is a potent inhibitor of TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily signalling. By binding to activated type I receptors, it prevents the activation of R-Smads (receptor-regulated Smads). To identify new components of the Smad pathway, we performed yeast two-hybrid screening using Smad7 as bait, and identified NEDD4-2 (neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4-2) as a direct binding partner of Smad7. NEDD4-2 is structurally similar to Smurfs (Smad ubiquitin regulatory factors) 1 and 2, which were identified previously as E3 ubiquitin ligases for R-Smads and TGF-beta superfamily receptors. NEDD4-2 functions like Smurfs 1 and 2 in that it associates with TGF-beta type I receptor via Smad7, and induces its ubiquitin-dependent degradation. Moreover, NEDD4-2 bound to TGF-beta-specific R-Smads, Smads 2 and 3, in a ligand-dependent manner, and induced degradation of Smad2, but not Smad3. However, in contrast with Smurf2, NEDD4-2 failed to induce ubiquitination of SnoN (Ski-related novel protein N), although NEDD4-2 bound to SnoN via Smad2 more strongly than Smurf2. We showed further that overexpressed NEDD4-2 prevents transcriptional activity induced by TGF-beta and BMP, whereas silencing of the NEDD4-2 gene by siRNA (small interfering RNA) resulted in enhancement of the responsiveness to TGF-beta superfamily cytokines. These data suggest that NEDD4-2 is a member of the Smurf-like C2-WW-HECT (WW is Trp-Trp and HECT is homologous to the E6-accessory protein) type E3 ubiquitin ligases, which negatively regulate TGF-beta superfamily signalling through similar, but not identical, mechanisms to those used by Smurfs.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling by WW domain-containing protein 1 (WWP1).Oncogene. 2004 Sep 9;23(41):6914-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207885. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15221015
-
Degradation of the tumor suppressor Smad4 by WW and HECT domain ubiquitin ligases.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 10;280(23):22115-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414027200. Epub 2005 Apr 6. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15817471
-
The N domain of Smad7 is essential for specific inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta signaling.J Cell Biol. 2001 Dec 10;155(6):1017-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200106023. Epub 2001 Dec 10. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11739411 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling.Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 2001 Nov;4(6):321-30. doi: 10.1006/mcbr.2001.0301. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11703090 Review.
-
Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases.Cancer Sci. 2008 Nov;99(11):2107-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00925.x. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18808420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TGF-β Signaling from Receptors to Smads.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Sep 1;8(9):a022061. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022061. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016. PMID: 27449815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nedd4L suppression in lung fibroblasts facilitates pathogenesis of lung fibrosis.Transl Res. 2023 Mar;253:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.10.002. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36257596 Free PMC article.
-
Gene profiling of SEC13, SMAD7, GHRL, long non-coding RNA GHRLOS, HIF-1α in gastric cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 21;12(1):6555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10402-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35449150 Free PMC article.
-
Informatics approaches to understanding TGFbeta pathway regulation.Development. 2009 Nov;136(22):3729-40. doi: 10.1242/dev.030320. Development. 2009. PMID: 19855015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PMEPA1/TMEPAI Is a Unique Tumorigenic Activator of AKT Promoting Proteasomal Degradation of PHLPP1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 30;13(19):4934. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194934. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. The transforming growth factor-βs. In: Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., editors. Peptide Growth Factors and Their Receptors, Part I. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1990. pp. 419–472.
-
- Heldin C.-H., Miyazono K., ten Dijke P. TGF-β signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature (London) 1997;390:465–471. - PubMed
-
- Massagué J. TGF-β signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:753–791. - PubMed
-
- Derynck R., Zhang Y., Feng X.-H. Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-β responses. Cell. 1998;95:737–740. - PubMed
-
- Attisano L., Wrana J. L. Smads as transcriptional co-modulators. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000;12:235–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

