Steady-state pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of donepezil hydrochloride in hepatically impaired patients
- PMID: 15496218
- PMCID: PMC1884555
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.01802.x
Steady-state pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of donepezil hydrochloride in hepatically impaired patients
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD), tolerability and safety of donepezil HCl 5 mg following oral doses for 1 and 24 days in hepatically impaired patients compared with healthy controls under steady-state, multiple-dose conditions.
Methods: In this single-centre, multiple-dose, open-label study, patients with impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh grade A or B) and healthy controls (matched by gender, age and weight to the hepatically impaired patients) received a single 5 mg dose of donepezil on day 1 and then donepezil HCl 5 mg once daily from days 6 to 29. PK and PD (determination of erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase inhibition) parameters were evaluated on days 1 and 29. Treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs), vital signs, physical examination and clinical laboratory test parameters were monitored throughout the study.
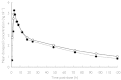
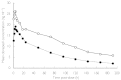
Results: A total of 35 subjects (18 patients with hepatic impairment and 17 healthy controls) were enrolled and 32 subjects (16 in each group) completed the study. On day 1 (following a single dose) hepatically impaired patients showed a significant decrease in T(max), while t((1/2)) and AUC(0-infinity) were significantly increased compared with the healthy controls. On day 29 (following multiple doses), AUC(0-24 h), C(max), t((1/2)), C(SS), and R(A) were significantly increased in hepatically impaired patients compared with healthy controls. AUC(0-24 h) increased by 47.6% in the patients with hepatic impairment compared with the healthy controls. There were no significant differences in PD between the groups, although at steady state, the mean AChE inhibition was 16.2% higher in the hepatically impaired patients. No serious AEs were reported and no subject withdrew from the study due to AEs. The most common AEs in both groups were headache and diarrhoea. No clinically significant changes from baseline were observed in vital signs, physical examination findings or electrocardiograms. There was a significant difference in the number of hepatically impaired subjects with abnormalities in serum glucose compared with healthy subjects. However, these elevations were not associated with AEs.
Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that patients with AD and mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh grade A or B) can be safely given donepezil 5 mg once daily and that this dose is associated with a nonsignificantly higher AChE inhibition than age-matched volunteers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concurrent administration of donepezil HCl and levodopa/carbidopa in patients with Parkinson's disease: assessment of pharmacokinetic changes and safety following multiple oral doses.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;58 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):41-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.01799.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15496222 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Steady-state pharmacokinetics and safety of donepezil HCl in subjects with moderately impaired renal function.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;58 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):18-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.01803.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15496219 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Concurrent administration of donepezil HCl and risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: assessment of pharmacokinetic changes and safety following multiple oral doses.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;58 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):50-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.01817.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15496223 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The safety and tolerability of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;58 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):1-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.01848.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15496217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of galantamine, a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, in healthy subjects and patients.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2010 May;5(2):115-24. doi: 10.2174/157488410791110805. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20156150 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic dosage assessment based on population pharmacokinetics of a novel single-dose transdermal donepezil patch in healthy volunteers.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Aug;71(8):967-77. doi: 10.1007/s00228-015-1875-2. Epub 2015 May 28. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26014587 Clinical Trial.
-
Adverse Drug Reactions of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in Older People Living with Dementia: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021 Sep 4;17:927-949. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S323387. eCollection 2021. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021. PMID: 34511919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of teriflunomide in Chinese adult patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis: A phase IV, 24-week multicenter study.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Feb 20;138(4):452-458. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002990. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 38311806 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenetic aspects of drugs used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 Apr;52(4):225-41. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0038-9. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23408070 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic changes of psychotropic drugs in patients with liver disease: implications for dose adaptation.Drug Saf. 2009;32(7):561-78. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200932070-00003. Drug Saf. 2009. PMID: 19530743 Review.
References
-
- Davies P, Maloney AJ. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1976;2:1403. - PubMed
-
- Dooley M, Lamb MM. Donepezil. A review of its use in Alzheimer's disease. Drugs Aging. 2000;16:199–226. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SL, Farlow MR, Doody RS, Mohs R, Friedhoff LT. A 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1998;50:136–45. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SL, Doody RS, Mohs RC, Friedhoff LT. Donepezil improves cognition and global function in Alzheimer disease. A 15-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:1021–31. - PubMed
-
- Burns A, Rossor M, Hecker J, Gauthier S, Petit H, Moller HJ, Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. The effects of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease – results from a multinational trial. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1999;10:237–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

