Vibrio vulnificus in Taiwan
- PMID: 15496235
- PMCID: PMC3320410
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1008.040047
Vibrio vulnificus in Taiwan
Abstract
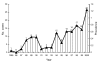
Residents in Taiwan are often exposed to marine microorganisms through seafood and occupational exposure. The number of reported cases of infection attributable to this organism has increased since the first case was reported in 1985. The increasing number of cases may be caused by greater disease activity or improved recognition by clinicians or laboratory workers. We analyze a clinical-case series of 84 patients with Vibrio vulnificus infection from 1995 to 2000 and describe the molecular epidemiologic features of pathogens isolated from these patients. The spectrum of clinical manifestations and outcomes, options of antimicrobial therapy, and virulence mechanisms were investigated. Results of molecular typing of isolates from humans and marine environment in this country had a high genetic divergence among these isolates. Education and measures are needed to prevent this emerging disease.
Figures

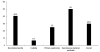
Similar articles
-
Assorted ribotypes of Vibrio vulnificus human and environmental isolates.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2010 Mar;63(2):116-8. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20332574
-
Epidemiologic study of Vibrio vulnificus infections by using variable number tandem repeats.Emerg Infect Dis. 2009 Aug;15(8):1282-5. doi: 10.3201/eid1508.080839. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19751592 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio vulnificus typing based on simple sequence repeats: insights into the biotype 3 group.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Sep;45(9):2951-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00236-07. Epub 2007 Jul 25. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17652479 Free PMC article.
-
[Noncholera vibrio infections (V. parahaemolyticus, V. vulnificus and others)].Nihon Rinsho. 2003 Mar;61 Suppl 3:811-22. Nihon Rinsho. 2003. PMID: 12718068 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Wound infections caused by Vibrio vulnificus and other marine bacteria.Epidemiol Infect. 2005 Jun;133(3):383-91. doi: 10.1017/s0950268805003894. Epidemiol Infect. 2005. PMID: 15962544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Severe septicemia, necrotizing fasciitis, and peritonitis due to Vibrio vulnificus in a patient undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Oct 14;15:422. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1163-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26467000 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic Diversity and Population Structure of Vibrio vulnificus Strains Isolated in Taiwan and Korea as Determined by Multilocus Sequence Typing.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 23;10(11):e0142657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142657. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26599487 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and population structure of Vibrio vulnificus on fishes from the northern Gulf of Mexico.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Nov;78(21):7611-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01646-12. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22923394 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of virulence markers among Vibrio vulnificus isolates of clinical and environmental origin and regional characteristics in Japan.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055219. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383115 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio vulnificus: An Environmental and Clinical Burden.Front Microbiol. 2017 May 31;8:997. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00997. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28620366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yuan CY, Yuan CC, Wei DC, Lee AM. Septicemia and gangrenous change of the legs caused by marine vibrio, Vibrio vulnificus—report of a case. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1987;86:448–51. - PubMed
-
- Lee SY, Chuang YC, Young CD. Extensive cellulitis with septic shock caused by Vibrio vulnificus infection—a case report with review of literature. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1991;65:1484–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
