Palmitoylation-dependent estrogen receptor alpha membrane localization: regulation by 17beta-estradiol
- PMID: 15496458
- PMCID: PMC539167
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0547
Palmitoylation-dependent estrogen receptor alpha membrane localization: regulation by 17beta-estradiol
Abstract
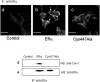
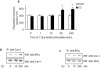
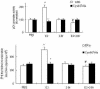
A fraction of the nuclear estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) is localized to the plasma membrane region of 17beta-estradiol (E2) target cells. We previously reported that ERalpha is a palmitoylated protein. To gain insight into the molecular mechanism of ERalpha residence at the plasma membrane, we tested both the role of palmitoylation and the impact of E2 stimulation on ERalpha membrane localization. The cancer cell lines expressing transfected or endogenous human ERalpha (HeLa and HepG2, respectively) or the ERalpha nonpalmitoylable Cys447Ala mutant transfected in HeLa cells were used as experimental models. We found that palmitoylation of ERalpha enacts ERalpha association with the plasma membrane, interaction with the membrane protein caveolin-1, and nongenomic activities, including activation of signaling pathways and cell proliferation (i.e., ERK and AKT activation, cyclin D1 promoter activity, DNA synthesis). Moreover, E2 reduces both ERalpha palmitoylation and its interaction with caveolin-1, in a time- and dose-dependent manner. These data point to the physiological role of ERalpha palmitoylation in the receptor localization to the cell membrane and in the regulation of the E2-induced cell proliferation.
Figures



References
-
- Acconcia, F., Ascenzi, P., Fabozzi, G., Visca, P., and Marino, M. (2004b). S-Palmitoylation modulates human estrogen receptor-α functions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 316, 878-883. - PubMed
-
- Acconcia, F., Totta, P., Ogawa, S., Cardillo, I., Inoue, S., Leone, S., Trentalance, A., Muramatsu, M., and Marino, M. (2004a). Survival versus apoptotic 17β-estradiol effect: role of ERα and ERβ activated non-genomic signalling. J. Cell. Physiol. Published online at www.interscience.wiley.com/DOI10.1002/5CP.20219. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitis, D. N., Wang, H., Bagshaw, R. D., Callahan, J. W., and Boggs, J. M. (2004). Membrane-associated estrogen receptor and caveolin-1 are present in central nervous system myelin and oligodendrocyte plasma membranes. J. Neurosci. Res. 75, 603-613. - PubMed
-
- Bijlmakers, M. J., and Marsh, M. (2003). The on-off story of protein palmitoylation. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 32-42. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 772, 248-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

