Two distinct Staufen isoforms in Xenopus are vegetally localized during oogenesis
- PMID: 15496522
- PMCID: PMC1370663
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.7450204
Two distinct Staufen isoforms in Xenopus are vegetally localized during oogenesis
Abstract
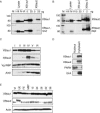
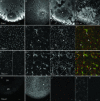
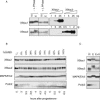
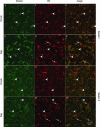
Localization of mRNA is an important way of generating early asymmetries in the developing embryo. In Drosophila, Staufen is intimately involved in the localization of maternally inherited mRNAs critical for cell fate determination in the embryo. We show that double-stranded RNA-binding Staufen proteins are present in the oocytes of a vertebrate, Xenopus, and are localized to the vegetal cytoplasm, a region where important mRNAs including VegT and Vg1 mRNA become localized. We identified two Staufen isoforms named XStau1 and XStau2, where XStau1 was found to be the principal Staufen protein in oocytes, eggs, and embryos, the levels of both proteins peaking during mid-oogenesis. In adults, Xenopus Staufens are principally expressed in ovary and testis. XStau1 was detectable throughout the oocyte cytoplasm by immunofluorescence and was concentrated in the vegetal cortical region from stage II onward. It showed partial codistribution with subcortical endoplasmic reticulum (ER), raising the possibility that Staufen may anchor mRNAs to specific ER-rich domains. We further showed that XStau proteins are transiently phosphorylated by the MAPK pathway during meiotic maturation, a period during which RNAs such as Vg1 RNA are released from their tight localization at the vegetal cortex. These findings provide evidence that Staufen proteins are involved in targeting and/or anchoring of maternal determinants to the vegetal cortex of the oocyte in Xenopus. The Xenopus oocyte should thus provide a valuable system to dissect the role of Staufen proteins in RNA localization and vertebrate development.
Figures



References
-
- Alarcon, V.B. and Elinson, R.P. 2001. RNA anchoring in the vegetal cortex of the Xenopus oocyte. J. Cell Sci. 114: 1731–1741. - PubMed
-
- Betley, J.N., Heinrich, B., Vernos, I., Sardet, C., Prodon, F., and Deshler, J.O. 2004. Kinesin II mediates Vg1 mRNA transport in Xenopus oocytes. Curr. Biol. 14: 219–224. - PubMed
-
- Braun, R.E. 1998. Post-transcriptional control of gene expression during spermatogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 9: 483–489. - PubMed
-
- Broadus, J., Fuerstenberg, S., and Doe, C.Q. 1998. Staufen-dependent localisation of prospero mRNA contributes to neuroblast daughter-cell fate. Nature 391: 792–795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
