Mash1 specifies neurons and oligodendrocytes in the postnatal brain
- PMID: 15496983
- PMCID: PMC526464
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600447
Mash1 specifies neurons and oligodendrocytes in the postnatal brain
Abstract
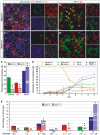
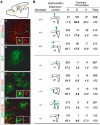
Progenitors in the telencephalic subventricular zone (SVZ) remain mitotically active throughout life, and produce different cell types at embryonic, postnatal and adult stages. Here we show that Mash1, an important proneural gene in the embryonic telencephalon, is broadly expressed in the postnatal SVZ, in progenitors for both neuronal and oligodendrocyte lineages. Moreover, Mash1 is required at birth for the generation of a large fraction of neuronal and oligodendrocyte precursors from the olfactory bulb. Clonal analysis in culture and transplantation experiments in postnatal brain demonstrate that this phenotype reflects a cell-autonomous function of Mash1 in specification of these two lineages. The conservation of Mash1 function in the postnatal SVZ suggests that the same transcription mechanisms operate throughout life to specify cell fates in this structure, and that the profound changes in the cell types produced reflect changes in the signalling environment of the SVZ.
Figures
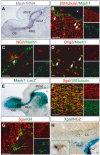
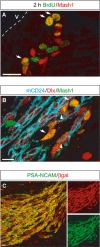
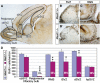
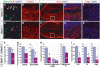
References
-
- Bertrand N, Castro DS, Guillemot F (2002) Proneural genes and the specification of neural cell types. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 517–530 - PubMed
-
- Casarosa S, Fode C, Guillemot F (1999) Mash1 regulates neurogenesis in the ventral telencephalon. Development 126: 525–534 - PubMed
-
- Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (1999) Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain [In Process Citation]. Cell 97: 703–716 - PubMed
-
- Doetsch F, Petreanu L, Caille I, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (2002) EGF converts transit-amplifying neurogenic precursors in the adult brain into multipotent stem cells. Neuron 36: 1021–1034 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

