Binding site for Robo receptors revealed by dissection of the leucine-rich repeat region of Slit
- PMID: 15496984
- PMCID: PMC526463
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600446
Binding site for Robo receptors revealed by dissection of the leucine-rich repeat region of Slit
Abstract
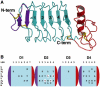
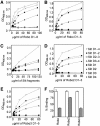
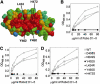
Recognition of the large secreted protein Slit by receptors of the Robo family provides fundamental signals in axon guidance and other developmental processes. In Drosophila, Slit-Robo signalling regulates midline crossing and the lateral position of longitudinal axon tracts. We report the functional dissection of Drosophila Slit, using structure analysis, site-directed mutagenesis and in vitro assays. The N-terminal region of Slit consists of a tandem array of four independently folded leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains, connected by disulphide-tethered linkers. All three Drosophila Robos were found to compete for a single highly conserved site on the concave face of the second LRR domain of Slit. We also found that this domain is sufficient for biological activity in a chemotaxis assay. Other Slit activities may require Slit dimerisation mediated by the fourth LRR domain. Our results show that a small portion of Slit is able to induce Robo signalling and indicate that the distinct functions of Drosophila Robos are encoded in their divergent cytosolic domains.
Figures
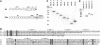

References
-
- Araujo SJ, Tear G (2003) Axon guidance mechanisms and molecules: lessons from invertebrates. Nat Rev Neurosci 4: 910–922 - PubMed
-
- Bashaw GJ, Kidd T, Murray D, Pawson T, Goodman CS (2000) Repulsive axon guidance: Abelson and Enabled play opposing roles downstream of the roundabout receptor. Cell 101: 703–715 - PubMed
-
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kidd T (1999) Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell 96: 795–806 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

