Increased CCR4 expression on circulating CD4(+) T cells in ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 15498047
- PMCID: PMC1809206
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02617.x
Increased CCR4 expression on circulating CD4(+) T cells in ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
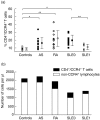
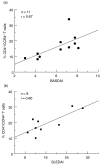
Previous studies have suggested that CCR4 is particularly important in the selective recruitment of various subsets of leucocytes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In this study, we examined the percentage of CD4(+)/CCR4(+) T cells within circulating lymphocytes in active ankylosing spondylitis (AS), RA and SLE patients. The clinical significance of CCR4 expression as well as possible associations between the expression and serum levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interferon (IFN)-gamma and interleukin (IL)-10 were also examined. Our results showed that the percentage of CD4(+)/CCR4(+) T cells was significantly elevated in AS and RA patients as compared with normal controls. The percentage was also significantly higher in SLE patients who had received no treatment with glucocorticoids or cytotoxic drugs (untreated SLE) than that in controls. In addition, the percentage of CD4(+)/CCR4(+) T cells showed significant positive correlations with the Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index (BASDAI) in AS and with the SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) in untreated SLE. Of all the cytokines examined, the elevated serum IL-10 level was closely correlated with the percentage of CD4(+)/CCR4(+) T cells in AS, RA and untreated SLE. These results suggest that CCR4 may be crucial in the pathogenesis of AS, RA and SLE. The percentage of CD4(+)/CCR4(+) T cells can serve as a useful marker for the activity of AS and untreated SLE.
Figures
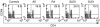
References
-
- Braun J, Bollow M, Neure L, et al. Usage of immunohistological and in situ hybridization techniques in the examination of sacroiliac joint biopsy specimens from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:499–505. - PubMed
-
- Kuroiwa T, Lee EG. Cellular interactions in the pathogenesis of lupus. the role of T cell and macrophages in the amplification of the inflammatory process in the kidney. Lupus. 1998;7:597–603. - PubMed
-
- Ruth JH, Rottman JB, Katschke KJ, Jr, et al. Selective lymphocyte chemokine receptor expression in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2750–60. - PubMed
-
- Katschke KJ, Jr, Rottman JB, Ruth JH, et al. Differential expression of chemokine receptors on peripheral blood, synovial fluid and synovial tissue monocytes/macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1022–32. - PubMed
-
- Hase K, Tani K, Shimizu T, Ohmoto Y, Matsushima K, Sone S. Increased CCR4 expression in active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Leukok Biol. 2001;70:749–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

