Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe, 1999-2002
- PMID: 15498166
- PMCID: PMC3320277
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1009.040069
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe, 1999-2002
Abstract
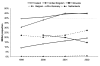
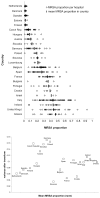
We explored the variation in proportions of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) between and within countries participating in the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System and temporal trends in its occurrence. This system collects routine antimicrobial susceptibility tests for S. aureus. We examined data collected from January 1999 through December 2002 (50,759 isolates from 495 hospitals in 26 countries). MRSA prevalence varied almost 100-fold, from <1% in northern Europe to >40% in southern and western Europe. MRSA proportions significantly increased in Belgium, Germany, Ireland, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom, and decreased in Slovenia. Within countries, MRSA proportions varied between hospitals with highest variance in countries with a prevalence of 5% to 20%. The observed trends should stimulate initiatives to control MRSA at national, regional, and hospital levels. The large differences between hospitals indicate that efforts may be most effective at regional and hospital levels.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO global strategy for containment of antimicrobial resistance. WHO/CDS/CSR/DRS/2001.2. Geneva: The Organization; 2001 [cited 21 Jan 2004]. Available from http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/drugresist/EGlobal_Strat.pdf
-
- Goettsch W, Bronzwaer SLAM, De Neeling AJ, Wale MC, Aubry-Damon H, Olsson-Liljequist B, et al. Standardization and quality assurance for antimicrobial resistance surveillance of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus within the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (EARSS). Clin Microbiol Infect. 2000;6:59–63. 10.1046/j.1469-0691.2000.00027.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
