The lipid-activated two-pore domain K+ channel TREK-1 is resistant to hypoxia: implication for ischaemic neuroprotection
- PMID: 15498799
- PMCID: PMC1665478
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.077503
The lipid-activated two-pore domain K+ channel TREK-1 is resistant to hypoxia: implication for ischaemic neuroprotection
Abstract
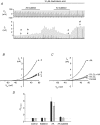
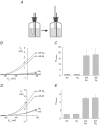
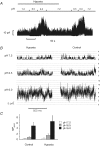
TREK-1 is a member of the two-pore domain potassium (K(2P)) channel family that is mechano-, heat, pH, voltage and lipid sensitive. It is highly expressed in the central nervous system and probably encodes one of the previously described arachidonic acid-activated K(+) channels. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and lysophospholipids protect the brain against global ischaemia. Since both lipids are openers of TREK-1, it has been suggested that this K(2P) channel is directly involved in neuroprotection. Recently, however, this view has been challenged by a report claiming that TREK-1 and its activation by arachidonic acid is inhibited by hypoxia. In the present study, we demonstrate that the bubbling of saline with gases results in the loss of arachidonic acid from solution. Using experimental conditions which obviate this experimental artefact we demonstrate that TREK-1 is resistant to hypoxia and is strongly activated by arachidonic acid even at low P(O(2)) (< 4 Torr). Furthermore, hypoxia fails to affect basal as well as 2,4,6-trinitrophenol- and acid-stimulated TREK-1 currents. These data are supportive for a possible role of TREK-1 in ischaemic neuroprotection and in cell signalling via arachidonic acid.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TREK-1, a K+ channel involved in neuroprotection and general anesthesia.EMBO J. 2004 Jul 7;23(13):2684-95. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600234. Epub 2004 Jun 3. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15175651 Free PMC article.
-
The stretch-activated potassium channel TREK-1 in rat cardiac ventricular muscle.Cardiovasc Res. 2006 Jan;69(1):86-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.08.018. Epub 2005 Oct 24. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. PMID: 16248991
-
Properties of single two-pore domain TREK-2 channels expressed in mammalian cells.J Physiol. 2007 Aug 15;583(Pt 1):57-69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.136150. Epub 2007 May 31. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17540699 Free PMC article.
-
TREK-1 K(+) channels in the cardiovascular system: their significance and potential as a therapeutic target.Cardiovasc Ther. 2012 Feb;30(1):e23-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00227.x. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Cardiovasc Ther. 2012. PMID: 20946320 Review.
-
Patents related to therapeutic activation of K(ATP) and K(2P) potassium channels for neuroprotection: ischemic/hypoxic/anoxic injury and general anesthetics.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009 Apr;19(4):433-60. doi: 10.1517/13543770902765151. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009. PMID: 19441925 Review.
Cited by
-
The human carotid body transcriptome with focus on oxygen sensing and inflammation--a comparative analysis.J Physiol. 2012 Aug 15;590(16):3807-19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.231084. Epub 2012 May 21. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22615433 Free PMC article.
-
The CNS under pathophysiologic attack--examining the role of K₂p channels.Pflugers Arch. 2015 May;467(5):959-72. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1664-2. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 25482672 Review.
-
Peripheral chemoreceptors: function and plasticity of the carotid body.Compr Physiol. 2012 Jan;2(1):141-219. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c100069. Compr Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23728973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of two zebrafish Twik related potassium channels, Kcnk2a and Kcnk2b.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 17;8(1):15311. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33664-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30333618 Free PMC article.
-
Tandem pore TWIK-related potassium channels and neuroprotection.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Aug;14(8):1293-1308. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.253506. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30964046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blondeau N, Lauritzen I, Widmann C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C. A potent protective role of lysophospholipids against global cerebral ischemia and glutamate excitotoxicity in neuronal cultures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002a;22:821–834. - PubMed
-
- Blondeau N, Widmann C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids induce ischemic and epileptic tolerance. Neuroscience. 2002b;109:231–241. - PubMed
-
- Duprat F, Lesage F, Patel AJ, Fink M, Romey G, Lazdunski M. The neuroprotective agent riluzole activates the two P domain K+ channels TREK-1 and TRAAK. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;57:906–912. - PubMed
-
- Fink M, Lesage F, Duprat F, Heurteaux C, Reyes R, Fosset M, et al. A neuronal two P domain K+ channel activated by arachidonic acid and polyunsaturated fatty acid. EMBO J. 1998;17:3297–3308. 10.1093/emboj/17.12.3297. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

