Heterogeneous expression of apolipoprotein-E by human macrophages
- PMID: 15500620
- PMCID: PMC1782582
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01972.x
Heterogeneous expression of apolipoprotein-E by human macrophages
Abstract
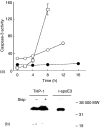
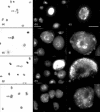
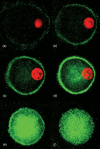
Apolipoprotein-E (apoE) is expressed at high levels by macrophages. In addition to its role in lipid transport, macrophage-derived apoE plays an important role in immunoregulation. Previous studies have identified macrophage subpopulations that differ substantially in their ability to synthesize specific cytokines and enzymes, however, potential heterogeneous macrophage apoE expression has not been studied. Here we examined apoE expression in human THP-1 macrophages and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM). Using immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry methods we reveal a striking heterogeneity in macrophage apoE expression in both cell types. In phorbol-ester-differentiated THP-1 macrophages, 5% of the cells over-expressed apoE at levels more than 50-fold higher than the rest of the population. ApoE over-expressing THP-1 macrophages contained condensed/fragmented nuclei and increased levels of activated caspase-3 indicating induction of apoptosis. In MDM, 3-5% of the cells also highly over-expressed apoE, up to 50-fold higher than the rest of the population; however, this was not associated with obvious nuclear alterations. The apoE over-expressing MDM were larger, more granular, and more autofluorescent than the majority of cells and they contained numerous vesicle-like structures that appeared to be coated by apoE. Flow cytometry experiments indicated that the apoE over-expressing subpopulation of MDM were positive for CD14, CD11b/Mac-1 and CD68. These observations suggest that specific macrophage subpopulations may be important for apoE-mediated immunoregulation and clearly indicate that subpopulation heterogeneity should be taken into account when investigating macrophage apoE expression.
Figures



References
-
- Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E. cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988;240:622. - PubMed
-
- Basu SK, Ho YK, Brown MS, Bilheimer DW, Anderson RG, Goldstein JL. Biochemical and genetic studies of the apoprotein E secreted by mouse macrophages and human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:9788. - PubMed
-
- Werb Z, Chin JR, Takemura R, Oropeza RL, Bainton DF, Stenberg P, Taylor JM, Reardon C. The cell and molecular biology of apolipoprotein E synthesis by macrophages. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;118:155. - PubMed
-
- Curtiss LK, Forte TM, Davis PA. Cord blood plasma lipoproteins inhibit mitogen-stimulated lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1984;133:1379. - PubMed
-
- Pepe MG, Curtiss LK. Apolipoprotein E is a biologically active constituent of the normal immunoregulatory lipoprotein, LDL-In. J Immunol. 1986;136:3716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
