Gene expression profiling of the developing Drosophila CNS midline cells
- PMID: 15501232
- PMCID: PMC2718736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.08.047
Gene expression profiling of the developing Drosophila CNS midline cells
Abstract
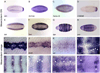
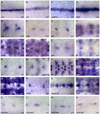
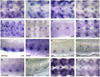
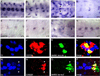
The Drosophila CNS midline cells constitute a specialized set of interneurons, motorneurons, and glia. The utility of the CNS midline cells as a neurogenomic system to study CNS development derives from the ability to easily identify CNS midline-expressed genes. For this study, we used a variety of sources to identify 281 putative midline-expressed genes, including enhancer trap lines, microarray data, published accounts, and the Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project (BDGP) gene expression data. For each gene, we analyzed expression at all stages of embryonic CNS development and categorized expression patterns with regard to specific midline cell types. Of the 281 candidates, we identified 224 midline-expressed genes, which include transcription factors, signaling proteins, and transposable elements. We find that 58 genes are expressed in mesectodermal precursor cells, 138 in midline primordium cells, and 143 in mature midline cells--50 in midline glia, 106 in midline neurons. Additionally, we identified 27 genes expressed in glial and mesodermal cells associated with the midline cells. This work provides the basis for future research that will generate a complete cellular and molecular map of CNS midline development, thus allowing for detailed genetic and molecular studies of neuronal and glial development and function.
Figures


References
-
- Araujo SJ, Tear G. Axon guidance mechanisms and molecules: lessons from invertebrates. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003;4:910–922. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf SI, Ip YT. The Snail protein family regulates neuroblast expression of inscuteable and string, genes involved in asymmetry and cell division in Drosophila. Development. 2001;128:4757–4767. - PubMed
-
- Bate CM, Grunewald EB. Embryogenesis of an insect nervous system II: a second class of neuron precursor cells and the origin of the intersegmental connectives. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1981;61:317–330. - PubMed
-
- Bennetzen JL. Transposable element contributions to plant gene and genome evolution. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000;42:251–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

