In vivo compartmentalization of functionally distinct, rapidly responsive antigen-specific T-cell populations in DNA-immunized or Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium-infected mice
- PMID: 15501769
- PMCID: PMC523063
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6390-6400.2004
In vivo compartmentalization of functionally distinct, rapidly responsive antigen-specific T-cell populations in DNA-immunized or Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium-infected mice
Abstract
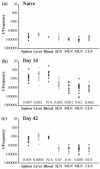
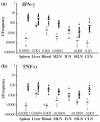
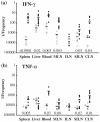
The location and functional properties of antigen-specific memory T-cell populations in lymphoid and nonlymphoid compartments following DNA immunization or infection with Salmonella were investigated. Epitope-specific CD8+ -T-cell expansion and retention during the memory phase were analyzed for DNA-immunized mice by use of a 5-h peptide restimulation assay. These data revealed that epitope-specific gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-positive CD8+ T cells occur at higher frequencies in the spleen, liver, and blood than in draining or peripheral lymph nodes during the expansion phase. Moreover, this distribution is maintained into long-term memory. The location and function of both CD4+ and CD8+ Salmonella-specific memory T cells in mice who were given a single dose of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium was also quantitated by an ex vivo restimulation with bacterial lysate to detect the total Salmonella-specific memory pool. Mice immunized up to 6 months previously with S. enterica serovar Typhimurium had bacterium-specific CD4+ T cells that were capable of producing IFN-gamma or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) at each site analyzed. Similar findings were observed for CD8+ T cells that were capable of producing IFN-gamma, while a much lower frequency and more restricted distribution were associated with TNF-alpha-producing CD8+ T cells. This study is the first to assess the frequencies, locations, and functions of both CD4+ and CD8+ memory T-cell populations in the same Salmonella-infected individuals and demonstrates the organ-specific functional compartmentalization of memory T cells after Salmonella infection.
Figures




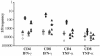
References
-
- Andersson, Å., W. J. Dai, J. P. Di Santo, and F. Brombacher. 1998. Early IFN-γ production and innate immunity during Listeria monocytogenes infection in the absence of NK cells. J. Immunol. 161:5600-5606. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., G. A. Corbin, and J. T. Harty. 2000. Cutting edge: OFF cycling of TNF production by antigen-specific CD8+ T cells is antigen independent. J. Immunol. 165:5387-5391. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., and J. T. Harty. 2000. Adaptive immunity and enhanced CD8+ T cell response to Listeria monocytogenes in the absence of perforin and IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 164:6444-6452. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., and J. T. Harty. 2000. Intracellular staining for TNF and IFN-gamma detects different frequencies of antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells. J. Immunol. Methods 238:107-117. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., B. B. Porter, and J. T. Harty. 2002. Programmed contraction of CD8 T cells after infection. Nat. Immunol. 3:619-626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

