Role of protein tyrosine kinase p53/56lyn in diminished lipopolysaccharide priming of formylmethionylleucyl- phenylalanine-induced superoxide production in human newborn neutrophils
- PMID: 15501776
- PMCID: PMC523037
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6455-6462.2004
Role of protein tyrosine kinase p53/56lyn in diminished lipopolysaccharide priming of formylmethionylleucyl- phenylalanine-induced superoxide production in human newborn neutrophils
Abstract
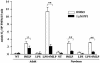
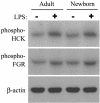
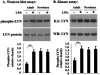
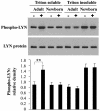
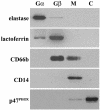
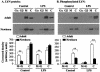
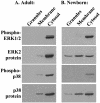
Human newborns are more susceptible than adults to bacterial infection. With gram-negative bacteria, this may be due to a diminished response of newborn leukocytes to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Since protein tyrosine kinase inhibition abolishes LPS priming in adult cells, we hypothesized that protein tyrosine kinases may have a critical role in LPS priming of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and that newborn PMNs may have altered protein tyrosine kinase activities. In the present study, we investigated the role of src family protein tyrosine kinases in the LPS response of newborn PMNs compared to adult cells. In a respiratory assay, the LPS-primed increase in formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (fMLP)-triggered O2- release by adult PMNs was greatly decreased by PP1 [4-amino-5-(4-methyphenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine], a src kinase inhibitor, to the level of untreated newborn PMNs, in which LPS failed to prime. LPS activated the src-like kinases p59hck (HCK) and p58fgr (FGR) in both adult and newborn PMNs but increased the activation of p53/56lyn (LYN) only in adult cells. In newborn PMNs, LYN was highly phosphorylated independent of LPS. We evaluated subcellular fractions of PMNs and found that the phosphorylated form of LYN was mainly in the Triton-extractable, cytosolic fraction in adult PMNs, while in newborn cells it was located mainly in Triton-insoluble, granule- and membrane-associated fractions. In contrast, the phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and p38 were mainly detected in the cytosol in both adult and newborn PMNs. These data indicate a role for LYN in the regulation of LPS priming. The trapping of phosphorylated LYN in the membrane-granule fraction in newborn PMNs may contribute to the deficiency of newborn cells in responding to LPS stimulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein- and CD14-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 by lipopolysaccharide in human neutrophils is associated with priming of respiratory burst.Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4068-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4068-4074.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117913 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Src family kinases p59/61hck and p58c-fgr results in defective adhesion-dependent neutrophil functions.J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(4):895-910. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.4.895. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8666673 Free PMC article.
-
The Src family kinases Hck and Fgr regulate neutrophil responses to N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine.J Immunol. 2007 Mar 15;178(6):3874-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.6.3874. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17339487 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-inflammatory effect of 2-(4-hydroxy-3-prop-2-enyl-phenyl)-4-prop-2-enyl-phenol by targeting Lyn kinase in human neutrophils.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Jul 5;236:90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 14. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25980585
-
Activation of SRC family kinases in human neutrophils. Evidence that p58C-FGR and p53/56LYN redistributed to a Triton X-100-insoluble cytoskeletal fraction, also enriched in the caveolar protein caveolin, display an enhanced kinase activity.FEBS Lett. 1996 Feb 12;380(1-2):198-203. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00029-4. FEBS Lett. 1996. PMID: 8603737
Cited by
-
Flice inhibitory protein is associated with the survival of neonatal neutrophils.Pediatr Res. 2011 Oct;70(4):327-31. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182290062. Pediatr Res. 2011. PMID: 21691254 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal and infantile immune responses to encapsulated bacteria and conjugate vaccines.Clin Dev Immunol. 2008;2008:628963. doi: 10.1155/2008/628963. Clin Dev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18825269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinase C Isozyme Immaturity/Deficiency in Cord Blood Monocytes and Neutrophils.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 30;25(21):11665. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111665. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519215 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal sepsis and neutrophil insufficiencies.Int Rev Immunol. 2010 Jun;29(3):315-48. doi: 10.3109/08830181003792803. Int Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20521927 Free PMC article.
-
O-GlcNAcylation: Crosstalk between Hemostasis, Inflammation, and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 13;25(18):9896. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189896. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337387 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

