Combined vaccine regimen based on parenteral priming with a DNA vaccine and administration of an oral booster consisting of a recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine strain for immunization against infection with human-derived enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains
- PMID: 15501779
- PMCID: PMC522993
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6480-6491.2004
Combined vaccine regimen based on parenteral priming with a DNA vaccine and administration of an oral booster consisting of a recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine strain for immunization against infection with human-derived enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains
Abstract
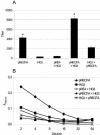
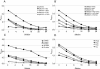
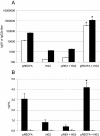
Repeated evidence has demonstrated that combined primer-booster immunization regimens can improve both secreted and humoral immune responses to antigens derived from viral, bacterial, and parasitic pathogens. For the present work, we evaluated the synergic serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) and fecal IgA antibody responses elicited in BALB/c mice who were intramuscularly primed with a DNA vaccine, pRECFA, followed by oral boosting with an attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine (HG3) strain, with both vaccines encoding the structural subunit (CfaB) of the CFA/I fimbriae produced by human-derived enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) strains. The immunological properties of the vaccine regimen were evaluated according to the order of the administered vaccines, the nature of the oral antigen carrier, the age of the vaccinated animals, the interval between the priming and boosting doses, and the amount of injected DNA. The production of gamma interferon and the IgG2a subclass in serum indicated that mice immunized with the primer-booster regimen developed prevailing type 1 T-cell-dependent immune responses. The synergic effect of the vaccine regimen on the induced antibody responses was also revealed by its ability to block the adhesive properties of CFA/I fimbriae expressed by live bacteria, as shown by the inhibition of Caco-2 cell and human erythrocyte binding. Moreover, DBA2 newborn mice were protected from lethal challenges with a CFA/I+ ETEC strain after the incubation of live bacteria with serum samples harvested from mice who were subjected to the primer-booster regimen. We propose, therefore, that the DNA primer-Salmonella booster regimen represents an alternative for the development of vaccines requiring both mucosal and systemic antibody responses for immunological protection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prime-boost vaccine regimen confers protective immunity to human-derived enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Vaccine. 2005 Mar 31;23(19):2430-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.11.026. Vaccine. 2005. PMID: 15752829
-
Boosting systemic and secreted antibody responses in mice orally immunized with recombinant Bacillus subtilis strains following parenteral priming with a DNA vaccine encoding the enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) CFA/I fimbriae B subunit.Vaccine. 2008 Jul 29;26(32):3998-4005. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.05.030. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18597902
-
Construction of non-toxic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae strains expressing high and immunogenic levels of enterotoxigenic E. coli colonization factor I fimbriae.Vaccine. 2008 Feb 6;26(6):743-52. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.12.009. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18191006
-
Strategies to overexpress enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) colonization factors for the construction of oral whole-cell inactivated ETEC vaccine candidates.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Mar;93(6):2291-300. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-3930-6. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22350259 Review.
-
New vaccine strategies against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. I: DNA vaccines against the CFA/I fimbrial adhesin.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999 Feb;32(2):223-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1999000200011. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999. PMID: 10347758 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in peste des petits ruminants vaccines.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Jul;206:91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.01.010. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28161212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A DNA vaccine encoding the enterohemorragic Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin 2 A2 and B subunits confers protective immunity to Shiga toxin challenge in the murine model.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 May;16(5):712-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00328-08. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19176691 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CS21 pilus contributes to adhesion to intestinal cells and to pathogenesis under in vivo conditions.Microbiology (Reading). 2013 Aug;159(Pt 8):1725-1735. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.065532-0. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Microbiology (Reading). 2013. PMID: 23760820 Free PMC article.
-
Glyco-engineered cell line and computational docking studies reveals enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CFA/I fimbriae bind to Lewis a glycans.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 26;8(1):11250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29258-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30050155 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal vaccination with a fimbrial tip adhesin and passive protection of neonatal mice against lethal human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge.Infect Immun. 2015 Dec;83(12):4555-64. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00858-15. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26371126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves, A. M. B., M. O. Lasaro, D. F. Almeida, and L. C. S. Ferreira. 1998. Epitope specificity of antibodies raised against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CFA/I fimbriae in mice immunized with naked DNA. Vaccine 16:9-15. - PubMed
-
- Amara, R. R., F. Villinger, J. D. Altman, S. L. Lydy, S. P. O'Neil, S. I. Staprans, D. C. Montefiori, Y. Xu, J. G. Herndon, L. S. Wyatt, M. A. Candido, N. L. Kozyr, R. L. Earl, J. M. Smith, H. L. Ma, B. D. Grimm, M. L. Hulsey, J. Miller, H. M. McClure, J. M. McNicholl, B. Moss, and H. L. Robinson. 2001. Control of a mucosal challenge and prevention of AIDS by a multiprotein DNA/MVA vaccine. Science 292:69-74. - PubMed
-
- Barry, E. M., Z. Altboum, G. Losonsky, and M. M. Levine. 2003. Immune responses elicited against multiple enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbriae and mutant LT expressed in attenuated Shigella vaccine strains. Vaccine 21:333-340. - PubMed
-
- Black, R. E. 1990. Epidemiology of traveller's diarrhea and relative importance of various pathogens. Rev. Infect. Dis. 12:S73-S79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

