Enhanced immunogenicity in the murine airway mucosa with an attenuated Salmonella live vaccine expressing OprF-OprI from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 15501786
- PMCID: PMC523058
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6546-6553.2004
Enhanced immunogenicity in the murine airway mucosa with an attenuated Salmonella live vaccine expressing OprF-OprI from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
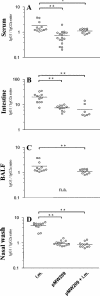
We constructed an oral live vaccine based on the attenuated aroA mutant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strain SL3261 expressing outer membrane proteins F and I (OprF-OprI) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and investigated it in a mouse model. Strains with in vivo inducible protein expression with the PpacC promoter showed good infection rates and immunogenicity but failed to engender detectable antibodies in the lung. However, a systemic booster vaccination following an oral primary immunization yielded high immunoglobulin A (IgA) and IgG antibody levels in both upper and lower airways superior to conventional systemic or mucosal booster vaccination alone. In addition, the proportion of IgG1 and IgG2a antibodies suggested that the systemic booster does not alter the more TH1-like type of response induced by the oral Salmonella primary vaccination. We conclude that an oral primary systemic booster vaccination strategy with an appropriate mucosal vector may be advantageous in diseases with the risk of P. aeruginosa airway infection, such as cystic fibrosis.
Figures
References
-
- Allen, J. S., G. Dougan, and R. A. Strugnell. 2000. Kinetics of the mucosal antibody secreting cell response and evidence of specific lymphocyte migration to the lung after oral immunisation with attenuated S. enterica var. typhimurium. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 27:275-281. - PubMed
-
- Baud, D., J. Benyacoub, V. Revaz, M. Kok, F. Ponci, M. Bobst, R. Curtiss III, P. De Grandi, and D. Nardelli-Haefliger. 2004. Immunogenicity against human papillomavirus type 16 virus-like particles is strongly enhanced by the PhoPc phenotype in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 72:750-756. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boucher, R. C. 2004. New concepts of the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 23:146-158. - PubMed
-
- Brennan, A. L., and D. M. Geddes. 2002. Cystic fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 15:175-182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

