Human factor in Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage
- PMID: 15501803
- PMCID: PMC523019
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6685-6688.2004
Human factor in Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage
Abstract
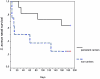
Persistent nasal carriers and noncarriers of Staphylococcus aureus were inoculated with a mixture of different S. aureus strains. The majority of noncarriers and nearly all persistent carriers returned to their original carrier state after artificial inoculation. Furthermore, the majority of persistent carriers tested positive again for their original resident strain. Using a human nasal inoculation model, we here demonstrate that the human factor is an important determinant of S. aureus nasal carriage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reclassification of Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage types.J Infect Dis. 2009 Jun 15;199(12):1820-6. doi: 10.1086/599119. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19419332
-
Effect of mupirocin treatment on nasal, pharyngeal, and perineal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in healthy adults.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Apr;49(4):1465-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.4.1465-1467.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15793127 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
What determines nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus?Trends Microbiol. 2001 Dec;9(12):605-10. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(01)02254-5. Trends Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11728874 Review.
-
Typing of Staphylococcus aureus colonising human nasal carriers by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.J Med Microbiol. 1995 Feb;42(2):127-32. doi: 10.1099/00222615-42-2-127. J Med Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7869348
-
The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus burn wound colonization.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2009 Oct;57(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2009.00565.x. Epub 2009 May 27. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19486150 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo competition and horizontal gene transfer among distinct Staphylococcus aureus lineages as major drivers for adaptational changes during long-term persistence in humans.BMC Microbiol. 2018 Oct 22;18(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1308-3. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30348081 Free PMC article.
-
Improving mathematical modeling of interventions to prevent healthcare-associated infections by interrupting transmission or pathogens: How common modeling assumptions about colonized individuals impact intervention effectiveness estimates.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 28;17(2):e0264344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264344. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35226689 Free PMC article.
-
Are nasal carriers of Staphylococcus aureus more likely to become colonized or infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on admission to a hospital?J Clin Microbiol. 2011 Jan;49(1):430-2. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02039-10. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20980558 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae interaction and response to pneumococcal vaccination: Myth or reality?Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016;12(2):351-7. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1081321. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 26905680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recurrent microbial keratitis and endogenous site Staphylococcus aureus colonisation.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 29;10(1):18559. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75821-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33122810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aly, R., H. R. Shinefield, C. Litz, and H. I. Maibach. 1980. Role of teichoic acid in the binding of Staphylococcus aureus to nasal epithelial cells. J. Infect. Dis. 141:463-465. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-Esther, C. A. 1976. Carriage patterns of Staphylococcus aureus in a healthy non-hospital population of adults and children. Ann. Hum. Biol. 3:221-227. - PubMed
-
- Bogaert, D., A. van Belkum, M. Sluijter, A. Luijendijk, R. de Groot, H. C. Rümke, H. A. Verbrugh, and P. W. Hermans. 2004. Colonisation by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in healthy children. Lancet 363:1871-1872. - PubMed
-
- Bruun, J. N. 1970. Post-operative wound infection: predisposing factors and the effect of a reduction in dissemination of staphylococci. Acta Med. Scand. 514:1-89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

