In vitro and in vivo evaluation of staphylococcal superantigen peptide antagonists
- PMID: 15501813
- PMCID: PMC522998
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6733-6737.2004
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of staphylococcal superantigen peptide antagonists
Abstract
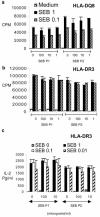
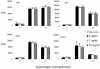
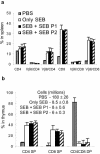
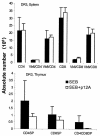
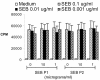
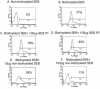
Superantigen peptide antagonists failed to block T-cell activation and cytokine production as well as toxic shock induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) in HLA class II transgenic mice. They also failed to inhibit the binding of SEB to HLA class II molecules as well as activation of human T lymphocytes in vitro.
Figures
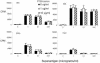
Similar articles
-
Expression and function of HLA-DR3 and DQ8 in transgenic mice lacking functional H2-M.Tissue Antigens. 2003 Aug;62(2):149-61. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00088.x. Tissue Antigens. 2003. PMID: 12889995
-
Major histocompatibility complex class II-associated peptides determine the binding of the superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin-1.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Oct;25(10):2894-8. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251028. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7589089
-
Human CD4 and human major histocompatibility complex class II (DQ6) transgenic mice: supersensitivity to superantigen-induced septic shock.Eur J Immunol. 1996 May;26(5):1074-82. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260518. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8647170
-
Chemotherapeutics targeting immune activation by staphylococcal superantigens.Med Sci Monit. 2005 Sep;11(9):RA290-5. Epub 2005 Aug 26. Med Sci Monit. 2005. PMID: 16127375 Review.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR, a pathway less recognized for staphylococcal superantigen-induced toxicity.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Nov 15;4(11):1343-66. doi: 10.3390/toxins4111343. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23202320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous HLA-DQ8αβ programs superantigens (SEG/SEI) to silence toxicity and unleash a tumoricidal network with long-term melanoma survival.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Oct;8(2):e001493. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001493. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33109631 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic down-modulators of staphylococcal superantigen-induced inflammation and toxic shock.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Aug;2(8):1963-83. doi: 10.3390/toxins2081963. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on staphylococcal superantigen-induced signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Sep 24;5(9):1629-54. doi: 10.3390/toxins5091629. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24064719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human leukocyte antigen class II transgenic mouse model unmasks the significant extrahepatic pathology in toxic shock syndrome.Am J Pathol. 2011 Jun;178(6):2760-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.02.033. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21641398 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal exposure to bacterial superantigens induces airway inflammation in HLA class II transgenic mice.Infect Immun. 2006 Feb;74(2):1284-96. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1284-1296.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16428778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arad, G., D. Hillman, R. Levy, and R. Kaempfer. 2004. Broad-spectrum immunity against superantigens is elicited in mice protected from lethal shock by a superantigen antagonist peptide. Immunol. Lett. 91:141-145. - PubMed
-
- Arad, G., D. Hillman, R. Levy, and R. Kaempfer. 2001. Superantigen antagonist blocks Th1 cytokine gene induction and lethal shock. J. Leukoc. Biol. 69:921-927. - PubMed
-
- Arad, G., R. Levy, D. Hillman, and R. Kaempfer. 2000. Superantigen antagonist protects against lethal shock and defines a new domain for T-cell activation. Nat. Med. 6:414-421. - PubMed
-
- DaSilva, L., B. C. Welcher, R. G. Ulrich, M. J. Aman, C. S. David, and S. Bavari. 2002. Humanlike immune response of human leukocyte antigen-DR3 transgenic mice to staphylococcal enterotoxins: a novel model for superantigen vaccines. J. Infect. Dis. 185:1754-1760. - PubMed
-
- Hong-Geller, E., and G. Gupta. 2003. Therapeutic approaches to superantigen-based diseases: a review. J. Mol Recognit. 16:91-101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

