Campylobacteriosis, Eastern Townships, Quebec
- PMID: 15504275
- PMCID: PMC3323265
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1010.040228
Campylobacteriosis, Eastern Townships, Quebec
Abstract
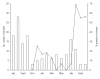
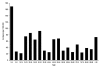
Independent risk factors for campylobacteriosis (eating raw, rare, or undercooked poultry; consuming raw milk or raw milk products; and eating chicken or turkey in a commercial establishment) account for <50% of cases in Quebec. Substantial regional and seasonal variations in campylobacteriosis were not correlated with campylobacter in chickens and suggested environmental sources of infection, such as drinking water.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Campylobacteriosis in urban versus rural areas: a case-case study integrated with molecular typing to validate risk factors and to attribute sources of infection.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 26;8(12):e83731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083731. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386265 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal patterns of Campylobacter contamination on chicken and their relationship to campylobacteriosis cases in the United States.Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 Sep 2;208:114-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.05.018. Epub 2015 May 29. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26065728
-
Campylobacteriosis in the South Bohemian Region - a Recurrent Problem.Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2016 Fall;65(3):193-197. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2016. PMID: 27690477 English.
-
Current epidemiological issues in human campylobacteriosis.Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 2001;(30):85S-95S. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01357.x. Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11422564 Review. No abstract available.
-
Incidence and control of Campylobacter in foods.Microbiologia. 1993 Feb;9 Spec No:57-65. Microbiologia. 1993. PMID: 8484918 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of real-time molecular typing in the surveillance of Campylobacter enteritis and comparison of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles from chicken and human isolates.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Mar;43(3):1105-11. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.3.1105-1111.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15750069 Free PMC article.
-
Colonization of cattle intestines by Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter lanienae.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Sep;71(9):5145-53. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5145-5153.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16151098 Free PMC article.
-
Non food-related risk factors of campylobacteriosis in Canada: a matched case-control study.BMC Public Health. 2016 Sep 27;16(1):1016. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3679-4. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27677338 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-centre prospective case-control study of campylobacter infection in persons aged 5 years and older in Australia.Epidemiol Infect. 2008 Oct;136(10):1315-6; author reply 1316-8. doi: 10.1017/S0950268808000344. Epub 2008 Apr 15. Epidemiol Infect. 2008. PMID: 18412999 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hyperendemic Campylobacter jejuni in guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus) raised for food in a semi-rural community of Quito, Ecuador.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2016 Jun;8(3):382-7. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12396. Epub 2016 May 11. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27043446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neal KR, Slack RC. The autumn peak in Campylobacter gastroenteritis. Are the risk factors the same for travel- and UK-acquired Campylobacter infections? J Public Health Med. 1995;17:98–102. - PubMed
-
- Bryan FL, Doyle MP. Health risks and consequences of Salmonella and Campylobacter jejuni in raw poultry. J Food Prot. 1995;58:326–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
