A novel Na+ channel agonist, dimethyl lithospermate B, slows Na+ current inactivation and increases action potential duration in isolated rat ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 15504759
- PMCID: PMC1575928
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705969
A novel Na+ channel agonist, dimethyl lithospermate B, slows Na+ current inactivation and increases action potential duration in isolated rat ventricular myocytes
Abstract
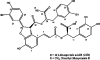
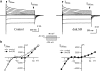
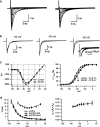
Voltage-gated Na(+) channel blockers have been widely used as local anaesthetics and antiarrhythmic agents. It has recently been proposed that Na(+) channel agonists can be used as inotropic agents. Here, we report the identification of a natural substance that acts as a Na(+) channel agonist. Using the patch-clamp technique in isolated rat ventricular myocytes, we investigated the electrophysiological effects of the substances isolated from the root extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza, which is known as 'Danshen' in Asian traditional medicine. By the intensive activity-guided fractionation, we identified dimethyl lithospermate B (dmLSB) as the most active component, while LSB, which is the major component of the extract, showed negligible electrophysiological effect. Action potential duration (APD(90)) was increased by 20 microM dmLSB from 58.8 +/- 12.1 to 202.3 +/- 9.5 ms. In spite of the prolonged APD, no early after-depolarization (EAD) was observed. dmLSB had no noticeable effect on K(+) or Ca(2+) currents, but selectively affected Na(+) currents (I(Na)). dmLSB slowed the inactivation kinetics of I(Na) by increasing the proportion of slowly inactivating component without inducing any persistent I(Na). The relative amplitude of slow component compared to the peak fast I(Na) was increased dose dependently by dmLSB (EC(50) = 20 microM). Voltage dependence of inactivation was not affected by dmLSB, while voltage dependence of activation shifted by 5 mV to the depolarised direction. Since the APD prolongation by dmLSB did not provoke EAD, which is thought as a possible mechanism for the proarrhythmia seen in other Na(+) channel agonists, dmLSB might be an excellent candidate for a Na(+) channel agonist.
British Journal of Pharmacology (2004).
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antiarrhythmic effects of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate, a novel sodium channel agonist in cultured neonatal rat ventricular myocytes.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Jan 1;85(1):69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.10.003. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23116965
-
Selective modulation of L-type calcium current by magnesium lithospermate B in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes.Life Sci. 2006 May 22;78(26):2989-97. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.11.024. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16376948
-
Action potential changes associated with a slowed inactivation of cardiac voltage-gated sodium channels by KB130015.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Aug;139(8):1469-79. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705379. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12922934 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of emigrated neutrophils on Na(+) and K(+) currents in rat ventricular myocytes.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006 Jan-Apr;90(1-3):249-69. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2005.07.003. Epub 2005 Aug 9. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16165196 Review.
-
A Na+ channel agonist: a potential cardiotonic agent with a novel mechanism?Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;143(6):663-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705970. Epub 2004 Oct 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15492018 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Effects of mixed herbal extracts from parched Puerariae radix, gingered Magnoliae cortex, Glycyrrhizae radix and Euphorbiae radix (KIOM-79) on cardiac ion channels and action potentials.J Korean Med Sci. 2009 Jun;24(3):403-12. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.3.403. Epub 2009 Jun 12. J Korean Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19543501 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing Effect of Insulin on Local Anesthetics-Induced Sciatic Nerve Block in Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Mar 11;2019:4252349. doi: 10.1155/2019/4252349. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30984781 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 1 regulates cardiac electrical activity by deacetylating the cardiac sodium channel.Nat Med. 2017 Mar;23(3):361-367. doi: 10.1038/nm.4284. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28191886 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular effects of salvianolic Acid B.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:247948. doi: 10.1155/2013/247948. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23840250 Free PMC article.
-
Fenpropathrin, a Widely Used Pesticide, Causes Dopaminergic Degeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Mar;53(2):995-1008. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9057-2. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25575680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CATERALL W.A. Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:15–43. - PubMed
-
- FUNG K.P., WU J., ZENG L.H., WONG H.N., LEE C.M., HON P.M., CHANG H.M., WU T.W. Lithospermic acid B as an antioxidant-based protector of cultured ventricular myocytes and aortic endothelial cells of rabbits. Life Sci. 1993;53:PL189–PL193. - PubMed
-
- KAMATA K., IIZUKA T., NAGAI M., KASUYA Y. Endothelium-dependent vasodilator effects of the extract from Salviae miltiorrhizae radix. A study on the identification of lithospermic acid B in the extracts. Gen Pharmacol. 1993;24:977–981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

