In vitro pharmacodynamic characteristics of amphotericin B, caspofungin, fluconazole, and voriconazole against bloodstream isolates of infrequent Candida species from patients with hematologic malignancies
- PMID: 15504881
- PMCID: PMC525414
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.11.4453-4456.2004
In vitro pharmacodynamic characteristics of amphotericin B, caspofungin, fluconazole, and voriconazole against bloodstream isolates of infrequent Candida species from patients with hematologic malignancies
Abstract
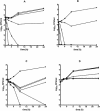
Time-kill and postantifungal effect (PAFE) of amphotericin B, caspofungin, fluconazole, and voriconazole were determined against clinical isolates of Candida guilliermondii, Candida kefyr, and Candida lusitaniae. Azoles displayed fungistatic activity and no measurable PAFE, regardless of the concentration tested. Amphotericin B and caspofungin demonstrated concentration-dependent fungicidal activity, although amphotericin B only produced a significant dose-dependent PAFE against all isolates tested.
Figures
References
-
- Cheng, M. F., K. W. Yu, R. B. Tang, Y. H. Fan, Y. L. Yang, K. S. Hsieh, M. Ho, and H. J. Lo. 2004. Distribution and antifungal susceptibility of Candida species causing candidemia from 1996 to 1999. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 48:33-37. - PubMed
-
- Clancy, C., M. Nguyen, and V. Yu. 1996. Fungemia caused by Candida lusitaniae. Infect. Med. 13:940, 948-951.
-
- Collin, B., C. J. Clancy, and M. H. Nguyen. 1999. Antifungal resistance in non-albicans Candida species. Drug Resist. Updat. 2:9-14. - PubMed
-
- Dick, J. D., R. R. Rosengard, W. G. Merz, R. K. Stuart, G. M. Hutchins, and R. Saval. 1985. Fatal disseminated candidiasis due to amphotericin B-resistant Candida guilliermondii. Ann. Intern. Med. 102:67-68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

