Clinical and neuropathologic variation in neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease
- PMID: 15505152
- PMCID: PMC3516854
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000139809.16817.dd
Clinical and neuropathologic variation in neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease
Abstract
Background: Recently described neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease (NIFID) shows considerable clinical heterogeneity.
Objective: To assess the spectrum of the clinical and neuropathological features in 10 NIFID cases.
Methods: Retrospective chart and comprehensive neuropathological review of these NIFID cases was conducted.
Results: The mean age at onset was 40.8 (range 23 to 56) years, mean disease duration was 4.5 (range 2.7 to 13) years, and mean age at death was 45.3 (range 28 to 61) years. The most common presenting symptoms were behavioral and personality changes in 7 of 10 cases and, less often, memory loss, cognitive impairment, language deficits, and motor weakness. Extrapyramidal features were present in 8 of 10 patients. Language impairment, perseveration, executive dysfunction, hyperreflexia, and primitive reflexes were frequent signs, whereas a minority had buccofacial apraxia, supranuclear ophthalmoplegia, upper motor neuron disease (MND), and limb dystonia. Frontotemporal and caudate atrophy were common. Histologic changes were extensive in many cortical areas, deep gray matter, cerebellum, and spinal cord. The hallmark lesions of NIFID were unique neuronal IF inclusions detected most robustly by antibodies to neurofilament triplet proteins and alpha-internexin.
Conclusion: NIFID is a neuropathologically distinct, clinically heterogeneous variant of frontotemporal dementia (FTD) that may include parkinsonism or MND. Neuronal IF inclusions are the neuropathological signatures of NIFID that distinguish it from all other FTD variants including FTD with MND and FTD tauopathies.
Figures

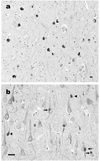
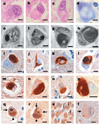

Comment in
-
NIFID: a new molecular pathology with a frontotemporal dementia phenotype.Neurology. 2004 Oct 26;63(8):1348-9. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000145112.90621.5e. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 15505145 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cairns NJ, Perry RH, Jaros E, et al. Patients with a novel neurofilamantopathy: dementia with neurofilament inclusions. Neurosci Lett. 2003;341:177–180. - PubMed
-
- Bigio EH, Lipton AM, White CL, III, et al. Frontotemporal dementia and motor neurone degeneration with neurofilament inclusion bodies: additional evidence for overlap between FTD and ALS. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2003;29:239–253. - PubMed
-
- Duyckaerts C, Mokhtari K, Fontaine B, et al. Maladie de Pick généralisée: une démence mal nommée caractérisée par des inclusions neurofilamentaires. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2003;159:219–219.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
