Conformational activation of Ca2+ entry by depolarization of skeletal myotubes
- PMID: 15505226
- PMCID: PMC524834
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0403485101
Conformational activation of Ca2+ entry by depolarization of skeletal myotubes
Abstract
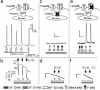
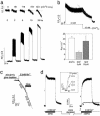
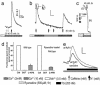
Store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) occurs in diverse cell types in response to depletion of Ca(2+) within the endoplasmic/sarcoplasmic reticulum and functions both to refill these stores and to shape cytoplasmic Ca(2+) transients. Here we report that in addition to conventional SOCE, skeletal myotubes display a physiological mechanism that we term excitation-coupled Ca(2+) entry (ECCE). ECCE is rapidly initiated by membrane depolarization. Like excitation-contraction coupling, ECCE is absent in both dyspedic myotubes that lack the skeletal muscle-type ryanodine receptor 1 and dysgenic myotubes that lack the dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR), and is independent of the DHPR l-type Ca(2+) current. Unlike classic SOCE, ECCE does not depend on sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) release. Indeed, ECCE produces a large Ca(2+) entry in response to physiological stimuli that do not produce substantial store depletion and depends on interactions among three different Ca(2+) channels: the DHPR, ryanodine receptor 1, and a Ca(2+) entry channel with properties corresponding to those of store-operated Ca(2+) channels. ECCE may provide a fundamental means to rapidly maintain Ca(2+) stores and control important aspects of Ca(2+) signaling in both muscle and nonmuscle cells.
Figures


References
-
- Ma, J. & Pan, Z. (2003) Front. Biosci. 8, D242-D255. - PubMed
-
- Putney, J. W., Broad, L. M., Braun, F.-J., Lievremont, J.-P. & Bird, G. S. J. (2001) J. Cell Sci. 114, 2223-2229. - PubMed
-
- Kiselyov, K., Shin, D. M., Wang, Y., Pessah, I. N., Allen, P. D. & Muallem, S. (2000) Mol. Cell 6, 421-431. - PubMed
-
- Kiselyov, K., Xu, X., Mozhayeva, G., Kuo, T., Pessah, I. N., Mignery, G., Zhu, Z., Birnbaumer, L. & Muallem, S. (1998) Nature 396, 478-482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

