Functional genomics analysis of Singapore grouper iridovirus: complete sequence determination and proteomic analysis
- PMID: 15507645
- PMCID: PMC525058
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.22.12576-12590.2004
Functional genomics analysis of Singapore grouper iridovirus: complete sequence determination and proteomic analysis
Abstract
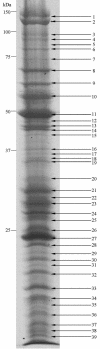
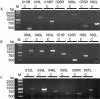
Here we report the complete genome sequence of Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV). Sequencing of the random shotgun and restriction endonuclease genomic libraries showed that the entire SGIV genome consists of 140,131 nucleotide bp. One hundred sixty-two open reading frames (ORFs) from the sense and antisense DNA strands, coding for lengths varying from 41 to 1,268 amino acids, were identified. Computer-assisted analyses of the deduced amino acid sequences revealed that 77 of the ORFs exhibited homologies to known virus genes, 23 of which matched functional iridovirus proteins. Forty-two putative conserved domains or signatures were detected in the National Center for Biotechnology Information CD-Search database and PROSITE database. An assortment of enzyme activities involved in DNA replication, transcription, nucleotide metabolism, cell signaling, etc., were identified. Viruses were cultured on a cell line derived from the embryonated egg of the grouper Epinephelus tauvina, isolated, and purified by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation. The protein extract from the purified virions was analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by in-gel digestion of protein bands. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry and database searching led to identification of 26 proteins. Twenty of these represented novel or previously unidentified genes, which were further confirmed by reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) and DNA sequencing of their respective RT-PCR products.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proteomic studies of the Singapore grouper iridovirus.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006 Feb;5(2):256-64. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M500149-MCP200. Epub 2005 Oct 31. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006. PMID: 16263702
-
Complete genome analysis of the mandarin fish infectious spleen and kidney necrosis iridovirus.Virology. 2001 Dec 5;291(1):126-39. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1208. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11878882
-
Complete genomic DNA sequence of rock bream iridovirus.Virology. 2004 Aug 1;325(2):351-63. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.05.008. Virology. 2004. PMID: 15246274
-
Identification of a novel marine fish virus, Singapore grouper iridovirus-encoded microRNAs expressed in grouper cells by Solexa sequencing.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 29;6(4):e19148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019148. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21559453 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence analysis of an iridovirus isolated from the orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides.Virology. 2005 Aug 15;339(1):81-100. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.05.021. Virology. 2005. PMID: 15964605
Cited by
-
Grouper interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) inhibits the infectivity of iridovirus and nodavirus by restricting viral entry.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Sep;104:172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32531330 Free PMC article.
-
Viral genomic methylation and the interspecies evolutionary relationships of ranavirus.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Nov 25;20(11):e1012736. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012736. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39585924 Free PMC article.
-
Viruses and Metabolism: The Effects of Viral Infections and Viral Insulins on Host Metabolism.Annu Rev Virol. 2021 Sep 29;8(1):373-391. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-091919-102416. Annu Rev Virol. 2021. PMID: 34586876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent host-shifts in ranaviruses: signatures of positive selection in the viral genome.J Gen Virol. 2013 Sep;94(Pt 9):2082-2093. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.052837-0. Epub 2013 Jun 19. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 23784445 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of a Megalocytivirus (family Iridoviridae) associated with turbot mortality in China.Virol J. 2010 Jul 15;7:159. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-159. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20630106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. M., and S. Cory. 1998. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322-1326. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J. S., and M. C. Whitby. 2003. The role of the SAP motif in promoting holliday junction binding and resolution by SpCCE1. J. Biol. Chem. 278:29121-29129. - PubMed
-
- Chan, Y. L., K. Suzuki, and I. G. Wool. 1995. The carboxyl extensions of two rat ubiquitin fusion proteins are ribosomal proteins S27a and L40. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 215:682-690. - PubMed
-
- Chew-Lim, M., G. H. Ngoh, M. K. Ng, J. M. Lee, P. Chew, J. Li, Y. C. Chan, and J. L. C. Howe. 1994. Grouper cell line for propagating grouper viruses. Singap. J. Prim. Ind. 22:113-116.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

