Plasmodium interspersed repeats: the major multigene superfamily of malaria parasites
- PMID: 15507685
- PMCID: PMC528792
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh907
Plasmodium interspersed repeats: the major multigene superfamily of malaria parasites
Abstract
Functionally related homologues of known genes can be difficult to identify in divergent species. In this paper, we show how multi-character analysis can be used to elucidate the relationships among divergent members of gene superfamilies. We used probabilistic modelling in conjunction with protein structural predictions and gene-structure analyses on a whole-genome scale to find gene homologies that are missed by conventional similarity-search strategies and identified a variant gene superfamily in six species of malaria (Plasmodium interspersed repeats, pir). The superfamily includes rif in P.falciparum, vir in P.vivax, a novel family kir in P.knowlesi and the cir/bir/yir family in three rodent malarias. Our data indicate that this is the major multi-gene family in malaria parasites. Protein localization of products from pir members to the infected erythrocyte membrane in the rodent malaria parasite P.chabaudi, demonstrates phenotypic similarity to the products of pir in other malaria species. The results give critical insight into the evolutionary adaptation of malaria parasites to their host and provide important data for comparative immunology between malaria parasites obtained from laboratory models and their human counterparts.
Figures
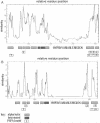
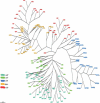
References
-
- Thornton J.W. and DeSalle,R. (2000) Gene family evolution and homology: genomics meets phylogenetics. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet., 1, 41–73. - PubMed
-
- Garnham P.C.C. (1966) Malaria Parasites and Other Haemosporidia. Blackwell, Oxford.
-
- Smith J.D., Chitnis,C.E., Craig,A.G., Roberts,D.J., Hudson-Taylor,D.E., Peterson,D.S., Pinches,R., Newbold,C.I. and Miller,L.H. (1995) Switches in expression of Plasmodium falciparum var genes correlate with changes in antigenic and cytoadherent phenotypes of infected erythrocytes. Cell, 82, 101–110. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng Q., Cloonan,N., Fischer,K., Thompson,J., Waine,G., Lanzer,M. and Saul,A. (1998) stevor and rif are Plasmodium falciparum multicopy gene families which potentially encode variant antigens. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol., 97, 161–176. - PubMed
-
- del Portillo H.A., Fernandez-Becerra,C., Bowman,S., Oliver,K., Preuss,M., Sanchez,C.P., Schneider,N.K., Villalobos,J.M., Rajandream,M.A., Harris,D. et al. (2001) A superfamily of variant genes encoded in the subtelomeric region of Plasmodium vivax. Nature, 410, 839–842. - PubMed

