An evaluation of UV protection imparted by cotton fabrics dyed with natural colorants
- PMID: 15509304
- PMCID: PMC526772
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-5945-4-15
An evaluation of UV protection imparted by cotton fabrics dyed with natural colorants
Abstract
Background: The ultraviolet properties of textiles dyed with synthetic dyes have been widely reported in literature. However, no study has investigated the ultraviolet properties of natural fabrics dyed with natural colorants. This study reports the Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) of cotton fabrics dyed with colorants of plant and insect origins.
Methods: Three cotton fabrics were dyed with three natural colorants. Fabrics were characterized with respect to fabric construction, weight, thickness and thread count. Influence of fabric characteristics on Ultraviolet Protection Factor was studied. Role of colorant concentration on the ultraviolet protection factor was examined via color strength analysis.
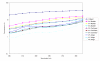
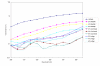
Results: A positive correlation was observed between the weight of the fabric and their UPF values. Similarly, thicker fabrics offered more protection from ultraviolet rays. Thread count appears to negatively correlate with UPF. Dyeing with natural colorants dramatically increased the protective abilities of all three fabric constructions. Additionally, within the same fabric type UPF values increased with higher depths of shade.
Conclusion: Dyeing cotton fabrics with natural colorants increases the ultraviolet protective abilities of the fabrics and can be considered as an effective protection against ultraviolet rays. The UPF is further enhanced with colorant of dark hues and with high concentration of the colorant in the fabric.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of ultraviolet transmission through cotton T-shirt fabrics with low ultraviolet protection by various laundering methods and dyeing: clinical implications.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001 May;44(5):767-74. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.112384. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001. PMID: 11312422
-
In vitro and in vivo determination of the UV protection factor for lightweight cotton and viscose summer fabrics: a preliminary study.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Dec;43(6):1009-16. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2000.107959. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 11100016
-
On the relationship between fabric processing and ultraviolet radiation transmission.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2007 Oct;23(5):191-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2007.00306.x. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2007. PMID: 17803598
-
The European standard for sun-protective clothing: EN 13758.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006 Feb;20(2):125-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2006.01401.x. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006. PMID: 16441617 Review.
-
Sun-protective clothing.J Cutan Med Surg. 1998 Jul;3(1):50-3. doi: 10.1177/120347549800300115. J Cutan Med Surg. 1998. PMID: 9677262 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Light on Lipid Peroxidation in SMOFlipid Mixtures During Storage, Transportation and Administration.Hosp Pharm. 2025 Feb 12:00185787251318281. doi: 10.1177/00185787251318281. Online ahead of print. Hosp Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39959184 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Degradation of Azo Dyes: Approaches and Prospects for a Hazard-Free Conversion by Microorganisms.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 14;19(8):4740. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19084740. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35457607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Color-changing intensified light-emitting multifunctional textiles via digital printing of biobased flavin.RSC Adv. 2020 Nov 22;10(69):42512-42528. doi: 10.1039/d0ra05533f. eCollection 2020 Nov 17. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35516780 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Ultraviolet-Protective Clothing.Cureus. 2022 Jul 27;14(7):e27333. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27333. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36043025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacité et innocuité des écrans solaires pour la prévention du cancer de la peau.CMAJ. 2021 Mar 8;193(10):E348-E354. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.201085-f. CMAJ. 2021. PMID: 33685958 Free PMC article. Review. French. No abstract available.
References
-
- Carcinogens listed in the tenth report http://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/roc/toc10.html
-
- Capjack L, Kerr N, Davis S, Fedosejevs R, Hatch KL, Markee NL. Protection of humans from ultraviolet radiation through the use of textiles: A Review. Family and Consumer Sciences Research Journal. 1994;23:198–218.
-
- Rieker J, Guschlbauer T, Rusmich S. Scientific and practical assessment of UV protection. Melliand Textilberichte. 2001;7–8:E155–156.
-
- Hatch KL. Fry not! ASTM Standarization News. 2001. pp. 18–21.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical