Roles and regulation of stat family transcription factors in human breast cancer
- PMID: 15509516
- PMCID: PMC1618660
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63403-7
Roles and regulation of stat family transcription factors in human breast cancer
Abstract
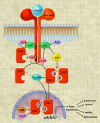
Stats (for signal transducers and activators of transcription) are a family of transcription factors that regulate cell growth and differentiation. Their activity is latent until phosphorylation by receptor-associated kinases. A sizable body of data from cell lines, mouse models, and human tissues now implicates these transcription factors in the oncogenesis of breast cancer. Because Stat activity is modulated by several posttranslational modifications and protein-protein interactions, these transcription factors are capable of integrating inputs from multiple signaling networks. Given this, the future utilization of Stats as prognostic markers and therapeutic targets in human breast cancer appears likely.
Figures

References
-
- Schindler C, Shuai K, Prezioso VR, Darnell JE. Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992;257:809–813. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE. The JAK-STAT pathway: summary of initial studies and recent advances. Rec Prog Horm Res. 1996;51:391–404. - PubMed
-
- Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell JE. Stat3: a Stat family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994;264:95–98. - PubMed
-
- Sadowski HB, Shuai K, Darnell JE, Gilman MZ. A common nuclear signal transduction pathway activated by growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science. 1993;261:1739–1744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

