Effects of angiotensin II receptor signaling during skin wound healing
- PMID: 15509535
- PMCID: PMC1618671
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63422-0
Effects of angiotensin II receptor signaling during skin wound healing
Abstract
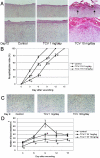
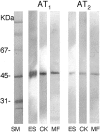
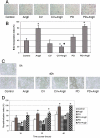
The tissue angiotensin (Ang) system, which acts independently of the circulating renin Ang system, is supposed to play an important role in tissue repair in the heart and kidney. In the skin, the role of the system for wound healing has remained to be ascertained. Our study demonstrated that oral administration of selective AngII type-1 receptor (AT(1)) blocker suppressed keratinocyte re-epithelization and angiogenesis during skin wound healing in rats. Immunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis indicated the existence of AT(1) and AngII type-2 receptor (AT(2)) in cultured keratinocytes and myofibroblasts. In a bromodeoxyuridine incorporation study, induction of AT(1) signaling enhanced the incorporation into keratinocytes and myofibroblasts. Wound healing migration assays revealed that induction of AT(1) signaling accelerated keratinocyte re-epithelization and myofibroblasts recovering. In these experiments, induction of AT(2) signaling acted vice versa. Taken together, our study suggests that skin wound healing is regulated by balance of opposing signals between AT(1) and AT(2).
Figures

References
-
- Gyurko R, Kimura B, Kurian P, Crews FT, Philips MI. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes play opposite roles in regulating phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in rat skin slices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;186:285–292. - PubMed
-
- Fujiyama S, Matsubara H, Nozawa Y, Maruyama K, Mori Y, Tsutsumi Y, Masaki H, Uchiyama Y, Koyama Y, Nose A, Iba O, Tateishi E, Ogata N, Jyo N, Higashiyama S, Iwasaka T. Angiotensin AT1 and AT2 receptors differentially regulate angiopoietin-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis by modulating heparin binding-epidermal growth factor (EGF)-mediated EGF receptor transactivation. Circ Res. 2001;88:22–29. - PubMed
-
- Shibasaki Y, Matsubara H, Nozawa Y, Mori Y, Masaki H, Kosaki A, Tsutsumi Y, Uchiyama Y, Fujiyama S, Nose A, Iba O, Tateishi E, Hasegawa T, Horiuchi M, Nahmias C, Iwasaka T. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation by increasing association of SHP-1 tyrosine phosphatase. Hypertension. 2001;38:367–372. - PubMed
-
- Murasawa S, Mori Y, Nozawa Y, Gotoh N, Shibuya M, Masaki H, Maruyama K, Tsutsumi Y, Moriguchi Y, Shibasaki Y, Tanaka Y, Iwasaka T, Inada M, Matsubara H. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-induced extracellular signal-related protein kinase activation is mediated by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor. Circ Res. 1998;82:1338–1348. - PubMed
-
- Eguchi S, Numaguchi K, Iwasaki H, Matsumoto T, Yamakawa T, Utsumonoa H, Motley ED, Kawakatsu H, Owada KM, Hirata Y, Marumo F, Inagami T. Calcium-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates the angiotensin II-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:8890–8896. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

