Enhanced accuracy in novel mirror drawing after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced proprioceptive deafferentation
- PMID: 15509758
- PMCID: PMC6730149
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1738-04.2004
Enhanced accuracy in novel mirror drawing after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced proprioceptive deafferentation
Abstract
When performing visually guided actions under conditions of perturbed visual feedback, e.g., in a mirror or a video camera, there is a spatial conflict between visual and proprioceptive information. Recent studies have shown that subjects without proprioception avoid this conflict and show a performance benefit. In this study, we tested whether deafferentation induced by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) can improve mirror tracing skills in normal subjects. Hand trajectory error during novel mirror drawing was compared across two groups of subjects that received either 1 Hz rTMS over the somatosensory cortex contralateral to the hand or sham stimulation. Mirror tracing was more accurate after rTMS than after sham stimulation. Using a position-matching task, we confirmed that rTMS reduced proprioceptive acuity and that this reduction was largest when the coil was placed at an anterior parietal site. It is thus possible, with rTMS, to enhance motor performance in tasks involving a visuoproprioceptive conflict, presumably by reducing the excitability of somatosensory cortical areas that contribute to the sense of hand position.
Figures
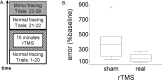

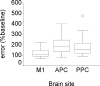
References
-
- Bard C, Fleury M, Teasdale N, Paillard J, Nougier V (1995) Contribution of proprioception for calibrating and updating the motor space. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 73: 246-254. - PubMed
-
- Boroojerdi B, Prager A, Muellbacher W, Cohen LG (2000) Reduction of human visual cortex excitability using 1-Hz transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 54: 1529-1531. - PubMed
-
- Chen R, Classen J, Gerloff C, Celnik P, Wassermann EM, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1997) Depression of motor cortex excitability by low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 48: 1398-1403. - PubMed
-
- Corkin S, Milner B, Rasmussen T (1970) Somatosensory thresholds—contrasting effects of postcentral-gyrus and posterior parietal-lobe excisions. Arch Neurol 23: 41-58. - PubMed
-
- Ghez C, Gordon J, Ghilardi MF (1995) Impairments of reaching movements in patients without proprioception. II. Effects of visual information on accuracy. J Neurophysiol 73: 361-372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
