Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-reactive oxygen species in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 15509775
- PMCID: PMC525474
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9695-9704.2004
Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-reactive oxygen species in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
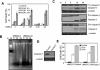
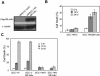
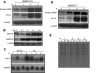
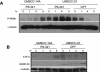
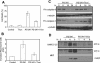
PS-341, also known as Velcade or Bortezomib, represents a new class of anticancer drugs which has been shown to potently inhibit the growth and/or progression of human cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Although it has been logically hypothesized that NF-kappaB is a major target of PS-341, the underlying mechanism by which PS-341 inhibits tumor cell growth is unclear. Here we found that PS-341 potently activated the caspase cascade and induced apoptosis in human HNSCC cell lines. Although PS-341 could inhibit NF-kappaB activation, the inhibition of NF-kappaB was not sufficient to initiate apoptosis in HNSCC cells. Using biochemical and microarray approaches, we found that proteasome inhibition by PS-341 induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in HNSCC cells. The inhibition of ROS significantly suppressed caspase activation and apoptosis induced by PS-341. Consistently, PS-341 could not induce the ER stress-ROS in PS-341-resistant HNSCC cells. Taken together, our results suggest that in addition to the abolishment of the prosurvival NF-kappaB, PS-341 might directly induce apoptosis by activating proapoptotic ER stress-ROS signaling cascades in HNSCC cells, providing novel insights into the PS-341-mediated antitumor activity.
Figures

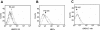
References
-
- Adams, J. 2003. The proteasome: structure, function, and role in the cell. Cancer Treat. Rev. 29(Suppl. 1):3-9. - PubMed
-
- Adams, J., V. J. Palombella, E. A. Sausville, J. Johnson, A. Destree, D. D. Lazarus, J. Mass, C. S. Pien, S. Prakash, and P. J. Elliot. 1999. Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 59:2615-2622. - PubMed
-
- Chen, S., A. Fribley, and C.-Y. Wang. 2002. Potentiation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of NF-κB inhibitor. J. Dent. Res. 81:98-102. - PubMed
-
- Fischer, H., U. Koenig, L. Eckhart, and E. Tschachler. 2002. Human caspase 12 has acquired deleterious mutations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293:722-726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
