Retinoid X receptor regulates Nur77/TR3-dependent apoptosis [corrected] by modulating its nuclear export and mitochondrial targeting
- PMID: 15509776
- PMCID: PMC525465
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9705-9725.2004
Retinoid X receptor regulates Nur77/TR3-dependent apoptosis [corrected] by modulating its nuclear export and mitochondrial targeting
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;25(1):524
Abstract
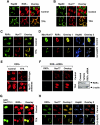
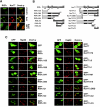
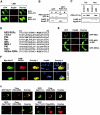
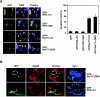
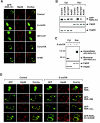
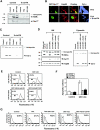
Retinoid X receptor (RXR) plays a central role in the regulation of intracellular receptor signaling pathways by acting as a ubiquitous heterodimerization partner of many nuclear receptors, including the orphan receptor Nur77 (also known as TR3 [corrected] or NGFI-B), which translocates from the nucleus to mitochondria, where it interacts with Bcl-2 to induce apoptosis. Here, we report that RXRalpha is required for nuclear export and mitochondrial targeting of Nur77 through their unique heterodimerization that is mediated by dimerization interfaces located in their DNA-binding domain. The effects of RXRalpha are attributed to a putative nuclear export sequence (NES) present in its carboxyl-terminal region. RXRalpha ligands suppress NES activity by inducing RXRalpha homodimerization or altering RXRalpha/Nur77 heterodimerization. The RXRalpha NES is also silenced by RXRalpha heterodimerization with retinoic acid receptor or vitamin D receptor. Consistently, we were able to show that the mitochondrial targeting of the RXRalpha/Nur77 heterodimer and its induction of apoptosis are potently inhibited by RXR ligands. Together, our results reveal a novel nongenotropic function of RXRalpha and its involvement in the regulation of the Nur77-dependent apoptotic pathway [corrected]
Figures





References
-
- Aarnisalo, P., C. H. Kim, J. W. Lee, and T. Perlmann. 2002. Defining requirements for heterodimerization between the retinoid X receptor and the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1. J. Biol. Chem. 277:35118-35123. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, C. T., P. Maruvada, G. L. Hager, and P. M. Yen. 2001. Nuclear cytoplasmic shuttling by thyroid hormone receptors. multiple protein interactions are required for nuclear retention. J. Biol. Chem. 276:11237-11245. - PubMed
-
- Bissonnette, R. P., T. Brunner, S. B. Lazarchik, N. J. Yoo, M. F. Boehm, D. R. Green, and R. A. Heyman. 1995. 9-cis retinoic acid inhibition of activation-induced apoptosis is mediated via regulation of fas ligand and requires retinoic acid receptor and retinoid X receptor activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:5576-5585. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bourguet, W., M. Ruff, P. Chambon, H. Gronemeyer, and D. Moras. 1995. Crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the human nuclear receptor RXR-α. Nature 375:377-382. - PubMed
-
- Bourguet, W., V. Vivat, J. M. Wurtz, P. Chambon, H. Gronemeyer, and D. Moras. 2000. Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains. Mol. Cell 5:289-298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
