Requirement of the Mre11 complex and exonuclease 1 for activation of the Mec1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 15509802
- PMCID: PMC525484
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.10016-10025.2004
Requirement of the Mre11 complex and exonuclease 1 for activation of the Mec1 signaling pathway
Abstract
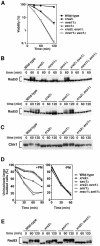
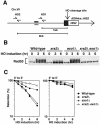
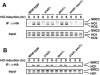
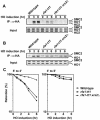
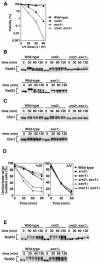
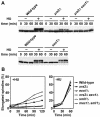
The large protein kinases, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ATM-Rad3-related (ATR), orchestrate DNA damage checkpoint pathways. In budding yeast, ATM and ATR homologs are encoded by TEL1 and MEC1, respectively. The Mre11 complex consists of two highly related proteins, Mre11 and Rad50, and a third protein, Xrs2 in budding yeast or Nbs1 in mammals. The Mre11 complex controls the ATM/Tel1 signaling pathway in response to double-strand break (DSB) induction. We show here that the Mre11 complex functions together with exonuclease 1 (Exo1) in activation of the Mec1 signaling pathway after DNA damage and replication block. Mec1 controls the checkpoint responses following UV irradiation as well as DSB induction. Correspondingly, the Mre11 complex and Exo1 play an overlapping role in activation of DSB- and UV-induced checkpoints. The Mre11 complex and Exo1 collaborate in producing long single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) tails at DSB ends and promote Mec1 association with the DSBs. The Ddc1-Mec3-Rad17 complex associates with sites of DNA damage and modulates the Mec1 signaling pathway. However, Ddc1 association with DSBs does not require the function of the Mre11 complex and Exo1. Mec1 controls checkpoint responses to stalled DNA replication as well. Accordingly, the Mre11 complex and Exo1 contribute to activation of the replication checkpoint pathway. Our results provide a model in which the Mre11 complex and Exo1 cooperate in generating long ssDNA tracts and thereby facilitate Mec1 association with sites of DNA damage or replication block.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cdc13 telomere capping decreases Mec1 association but does not affect Tel1 association with DNA ends.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Jun;18(6):2026-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-12-1074. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17377065 Free PMC article.
-
Sae2 antagonizes Rad9 accumulation at DNA double-strand breaks to attenuate checkpoint signaling and facilitate end resection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 18;115(51):E11961-E11969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816539115. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30510002 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Ku-mediated end joining suppresses mec1Delta lethality by depleting the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1 through a pathway controlled by Tel1 kinase and the Mre11 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(23):10652-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10652-10664.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16287875 Free PMC article.
-
Interplays between ATM/Tel1 and ATR/Mec1 in sensing and signaling DNA double-strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Oct;12(10):791-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Aug 13. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23953933 Review.
-
Activation of ATR-related protein kinase upon DNA damage recognition.Curr Genet. 2020 Apr;66(2):327-333. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-01039-w. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 31624858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hsp90 induces increased genomic instability toward DNA-damaging agents by tuning down RAD53 transcription.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Aug 1;27(15):2463-78. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-12-0867. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27307581 Free PMC article.
-
Dual role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Tel1 in the checkpoint response to double-strand breaks.EMBO Rep. 2007 Apr;8(4):380-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400911. Epub 2007 Mar 9. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17347674 Free PMC article.
-
ATR-binding lncRNA ScaRNA2 promotes cancer resistance through facilitating efficient DNA end resection during homologous recombination repair.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 30;42(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02829-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37775817 Free PMC article.
-
To trim or not to trim: progression and control of DSB end resection.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jun 15;12(12):1848-60. doi: 10.4161/cc.25042. Epub 2013 May 29. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23708517 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved function for a Caenorhabditis elegans Com1/Sae2/CtIP protein homolog in meiotic recombination.EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5071-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601916. Epub 2007 Nov 15. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 18007596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham, R. T. 2001. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 15:2177-2196. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist, C. J., and M. B. Kastan. 2003. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421:499-506. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez, V. P., L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, A. J. Cesare, Y. Maniwa, J. D. Griffith, J. Hurwitz, and A. Sancar. 2003. Loading of the human 9-1-1 checkpoint complex onto DNA by the checkpoint clamp loader hRad17-replication factor C complex in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:1633-1638. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan, S. W., J. Chang, J. Prescott, and E. H. Blackburn. 2001. Altering telomere structure allows telomerase to act in yeast lacking ATM kinases. Curr. Biol. 11:1240-1250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
