Deletion mapping of homoeologous group 6-specific wheat expressed sequence tags
- PMID: 15514044
- PMCID: PMC1448826
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.034843
Deletion mapping of homoeologous group 6-specific wheat expressed sequence tags
Abstract
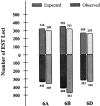
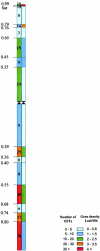
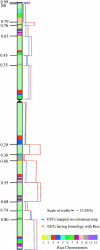
To localize wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) ESTs on chromosomes, 882 homoeologous group 6-specific ESTs were identified by physically mapping 7965 singletons from 37 cDNA libraries on 146 chromosome, arm, and sub-arm aneuploid and deletion stocks. The 882 ESTs were physically mapped to 25 regions (bins) flanked by 23 deletion breakpoints. Of the 5154 restriction fragments detected by 882 ESTs, 2043 (loci) were localized to group 6 chromosomes and 806 were mapped on other chromosome groups. The number of loci mapped was greatest on chromosome 6B and least on 6D. The 264 ESTs that detected orthologous loci on all three homoeologs using one restriction enzyme were used to construct a consensus physical map. The physical distribution of ESTs was uneven on chromosomes with a tendency toward higher densities in the distal halves of chromosome arms. About 43% of the wheat group 6 ESTs identified rice homologs upon comparisons of genome sequences. Fifty-eight percent of these ESTs were present on rice chromosome 2 and the remaining were on other rice chromosomes. Even within the group 6 bins, rice chromosomal blocks identified by 1-6 wheat ESTs were homologous to up to 11 rice chromosomes. These rice-block contigs were used to resolve the order of wheat ESTs within each bin.
Figures


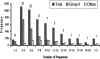
Similar articles
-
Analysis of expressed sequence tag loci on wheat chromosome group 4.Genetics. 2004 Oct;168(2):651-63. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034827. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15514042 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome bin map of expressed sequence tags in homoeologous group 1 of hexaploid wheat and homoeology with rice and Arabidopsis.Genetics. 2004 Oct;168(2):609-23. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034793. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15514039 Free PMC article.
-
A 2500-locus bin map of wheat homoeologous group 5 provides insights on gene distribution and colinearity with rice.Genetics. 2004 Oct;168(2):665-76. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034835. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15514043 Free PMC article.
-
A 2600-locus chromosome bin map of wheat homoeologous group 2 reveals interstitial gene-rich islands and colinearity with rice.Genetics. 2004 Oct;168(2):625-37. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034801. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15514040 Free PMC article.
-
Group 3 chromosome bin maps of wheat and their relationship to rice chromosome 1.Genetics. 2004 Oct;168(2):639-50. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034819. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15514041 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Construction and evaluation of cDNA libraries for large-scale expressed sequence tag sequencing in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Genetics. 2004 Oct;168(2):595-608. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034785. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15514038 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis and physical mapping of barley genes in wheat-barley chromosome addition lines.Genetics. 2006 Feb;172(2):1277-85. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.049908. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16322516 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of Brachypodium genome and its syntenic relationship with rice and wheat.Plant Mol Biol. 2009 May;70(1-2):47-61. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9456-3. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Plant Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19184460
-
Genetic rearrangements of six wheat-agropyron cristatum 6P addition lines revealed by molecular markers.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 4;9(3):e91066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091066. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24595330 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide diversity maps reveal variation in diversity among wheat genomes and chromosomes.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 14;11:702. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-702. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21156062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, M. D., J. M. Kelley, J. D. Gocayne, M. Dubnick, M. H. Polymeropoulos et al., 1991. Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science 252: 1651–1656. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, S., J. A. Anderson, M. E. Sorrells and S. D. Tanksley, 1993. Homoeologous relationships of rice, wheat and maize chromosomes. Mol. Gen. Genet. 241: 483–490. - PubMed

