Hypervariable genes--experimental error or hidden dynamics
- PMID: 15514108
- PMCID: PMC528822
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh146
Hypervariable genes--experimental error or hidden dynamics
Abstract
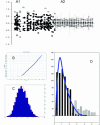
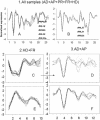
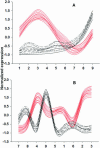
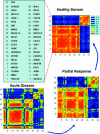
In a homogeneous group of samples, not all genes of high variability stem from experimental errors in microarray experiments. These expression variations can be attributed to many factors including natural biological oscillations or metabolic processes. The behavior of these genes can tease out important clues about naturally occurring dynamic processes in the organism or experimental system under study. We developed a statistical procedure for the selection of genes with high variability denoted hypervariable (HV) genes. After the exclusion of low expressed genes and a stabilizing log-transformation, the majority of genes have comparable residual variability. Based on an F-test, HV genes are selected as having a statistically significant difference from the majority of variability stabilized genes measured by the 'reference group'. A novel F-test clustering technique, further noted as 'F-means clustering', groups HV genes with similar variability patterns, presumably from their participation in a common dynamic biological process. F-means clustering establishes, for the first time, groups of co-expressed HV genes and is illustrated with microarray data from patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and healthy controls.
Figures
References
-
- Dozmorov I.M. and Centola,M. (2003) An associative analysis of gene expression array data. Bioinformatics, 19, 204–211. - PubMed
-
- Dooley S., Herlitzka,I., Hanselmann,R., Ermis,A., Henn,W., Remberger,K., Hopf,T. and Welter,C. (1996) Constitutive expression of c-fos and c-jun, overexpression of ets-2, and reduced expression of metastasis suppressor gene nm23-H1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis., 55, 298–304. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ohtani N., Zebedee,Z., Huot,T.J.G., Stinson,J.A., Sugimoto,M., Ohashi,Y., Sharrocks,A.D., Peters,G. and Hara,E. (2001) Opposing effects of Ets and Id proteins on p16 (INK4A) expression during cellular senescence. Nature, 409, 1067–1070. - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi K., Kohsaka,H., Inoue,N., Terada,Y., Ito,H., Hirokawa,K. and Miyasaka,N. (1999) Induction of the p16INK4a senescence gene as a new therapeutic strategy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Med., 5,760–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

