Myoglobin immunoassay utilizing directional surface plasmon-coupled emission
- PMID: 15516120
- PMCID: PMC6848856
- DOI: 10.1021/ac0491612
Myoglobin immunoassay utilizing directional surface plasmon-coupled emission
Abstract
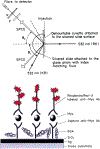
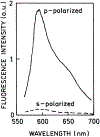
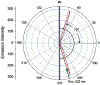
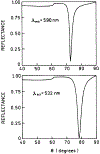
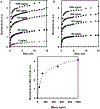
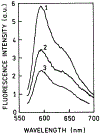
We described an immunoassay for the cardiac marker myoglobin on a thin silver mirror surface using surface plasmon-coupled emission (SPCE). SPCE occurs for fluorophores in proximity (within approximately 200 nm) of a thin metal film (in our case, silver) and results in a highly directional radiation through a glass substrate at a well-defined angle from the normal axis. We used the effect of SPCE to develop a myoglobin immunoassay on the silver mirror surface deposited on a glass substrate. Binding of the labeled anti-myoglobin antibodies led to the enhanced fluorescence emission at a specific angle of 72 degrees . The directional and enhanced directional fluorescence emission enables detection of myoglobin over a wide range of concentrations from subnormal to the elevated level of this cardiac marker. Utilizing SPCE allowed us also to demonstrate significant background suppression (from serum or whole blood) in the myoglobin immunoassay. We expect SPCE to become a powerful technique for performing immunoassays for many biomarkers in surface-bound assays.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasmonic technology: novel approach to ultrasensitive immunoassays.Clin Chem. 2005 Oct;51(10):1914-22. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.053199. Epub 2005 Jul 28. Clin Chem. 2005. PMID: 16055432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoassays based on directional surface plasmon-coupled emission.J Immunol Methods. 2004 Mar;286(1-2):133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2003.12.009. J Immunol Methods. 2004. PMID: 15087228 Free PMC article.
-
Directional surface plasmon-coupled emission: application for an immunoassay in whole blood.Anal Biochem. 2005 Sep 15;344(2):161-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2005.07.005. Anal Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16091280 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-wavelength immunoassays using surface plasmon-coupled emission.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jan 16;313(3):721-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.12.010. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 14697250 Free PMC article.
-
Surface plasmon-coupled emission: what can directional fluorescence bring to the analytical sciences?Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2012;5:317-36. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-062011-143208. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2012. PMID: 22524220 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of surface plasmon coupled emission to study of muscle.Biophys J. 2006 Oct 1;91(7):2626-35. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.088369. Epub 2006 Jul 14. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16844757 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave-Accelerated and Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence Myoglobin Detection on Silvered Surfaces: Potential Application to Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis.Plasmonics. 2006 Mar;1(1):53-59. doi: 10.1007/s11468-006-9006-7. Epub 2006 Mar 1. Plasmonics. 2006. PMID: 19444320 Free PMC article.
-
Use of surface plasmon-coupled emission for enhancing light transmission through Top-Emitting Organic Light Emitting Diodes.Thin Solid Films. 2008 Feb 29;516(8):1977-1983. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2007.05.081. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Thin Solid Films. 2008. PMID: 33828344 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmonic technology: novel approach to ultrasensitive immunoassays.Clin Chem. 2005 Oct;51(10):1914-22. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.053199. Epub 2005 Jul 28. Clin Chem. 2005. PMID: 16055432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescence Based on Surface Plasmon Coupled Emission for Ultrahigh Sensitivity Immunoassay of Cardiac Troponin I.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 21;9(5):448. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050448. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33919217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ellenius J; Groth T; Lindahl B; Wallentin L Clin. Chem 1997, 43, 1919–1925. - PubMed
-
- Malasky BR; Alpert JS Cardiol. Rev 2002, 10, 306–317. - PubMed
-
- Panteghini M Am. J. Clin. Pathol 2002, 118, 354–361. - PubMed
-
- Di Serio F; Antonelli G; Trerotoli P; Tampoia M; Matarrese A; Pansini N Clin. Chim. Acta, 2003, 333, 185–189. - PubMed
-
- Gibler WB; Blomkalns AL; Collins SP Rev. Cardiovasc. Med 2003, 4, S47–S55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

