Molecular physiological analysis of the two plastidic ATP/ADP transporters from Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15516503
- PMCID: PMC527152
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.049502
Molecular physiological analysis of the two plastidic ATP/ADP transporters from Arabidopsis
Abstract
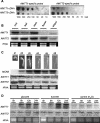
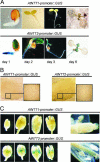
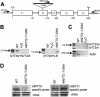
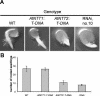
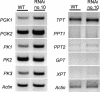
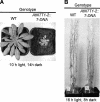
Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) possesses two isoforms of plastidic ATP/ADP transporters (AtNTT1 and AtNTT2) exhibiting similar biochemical properties. To analyze the function of both isoforms on the molecular level, we examined the expression pattern of both genes by northern-blot analysis and promoter-beta-glucuronidase fusions. AtNTT1 represents a sugar-induced gene mainly expressed in stem and roots, whereas AtNTT2 is expressed in several Arabidopsis tissues with highest accumulation in developing roots and young cotyledons. Developing lipid-storing seeds hardly contained AtNTT1 or -2 transcripts. The absence of a functional AtNTT1 gene affected plant development only slightly, whereas AtNTT2T-DNA, AtNTT1-2T-DNA, and RNA interference (RNAi) plants showed retarded plant development, mainly characterized by a reduced ability to generate primary roots and a delayed chlorophyll accumulation in seedlings. Electron microscopic examination of chloroplast substructure also revealed an impaired formation of thylakoids in RNAi seedlings. Moreover, RNAi- and AtNTT1-2T-DNA plants showed reduced accumulation of the nuclear-encoded protein CP24 during deetiolation. Under short-day conditions reduced plastidic ATP import capacity correlates with a substantially reduced plant growth rate. This effect is absent under long-day conditions, strikingly indicating that nocturnal ATP import into chloroplasts is important. Plastidic ATP/ADP transport activity exerts significant control on lipid synthesis in developing Arabidopsis seeds. In total we made the surprising observation that plastidic ATP/ADP transport activity is not required to pass through the complete plant life cycle. However, plastidic ATP/ADP-transporter activity is required for both an undisturbed development of young tissues and a controlled cellular metabolism in mature leaves.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The plastidic DEAD-box RNA helicase 22, HS3, is essential for plastid functions both in seed development and in seedling growth.Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Sep;54(9):1431-40. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct091. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23803517
-
Occurrence of two plastidic ATP/ADP transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana L.--molecular characterisation and comparative structural analysis of similar ATP/ADP translocators from plastids and Rickettsia prowazekii.Eur J Biochem. 1998 Mar 15;252(3):353-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2520353.x. Eur J Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9546649
-
Expression of a plastidic ATP/ADP transporter gene in Escherichia coli leads to a functional adenine nucleotide transport system in the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane.J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 17;273(16):9630-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.16.9630. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9545295
-
Non-mitochondrial ATP transport.Trends Biochem Sci. 1999 Feb;24(2):64-8. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(98)01334-6. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999. PMID: 10098400 Review.
-
Molecular biology of the plastidic phosphorylated serine biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana.Amino Acids. 2001;20(3):243-59. doi: 10.1007/s007260170042. Amino Acids. 2001. PMID: 11354602 Review.
Cited by
-
Live imaging of inorganic phosphate in plants with cellular and subcellular resolution.Plant Physiol. 2015 Mar;167(3):628-38. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.254003. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25624397 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated physiological and weighted gene co-expression network analysis reveals the hub genes engaged in nitrate-regulated alleviation of ammonium toxicity at the seedling stage in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 17;13:1012966. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1012966. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36466221 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of malate valve capacities lead to improved N-assimilation and growth in transgenic A. thaliana plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2014;9(7):e29057. doi: 10.4161/psb.29057. Plant Signal Behav. 2014. PMID: 25763488 Free PMC article.
-
Increased activity of the vacuolar monosaccharide transporter TMT1 alters cellular sugar partitioning, sugar signaling, and seed yield in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2010 Oct;154(2):665-77. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.162040. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20709831 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of chloroplastic adenylate kinases in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2008 Feb;146(2):492-504. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.114702. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18162585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker D, Kemper E, Schell J, Masterson R (1992) New plant binary vectors with selectable markers located proximal to the left T-DNA border. Plant Mol Biol 20: 1195–1197 - PubMed
-
- Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL (2000) Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, MD
-
- Drgon T, Sabova L, Nelson N, Kolarov J (1991) ADP/ATP translocator is essential only for anaerobic growth of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 289: 159–162 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

